Did you know about 80% of women who get a breast biopsy don’t have breast cancer? This fact shows how important biopsies are. They provide clear answers when there’s doubt. A biopsy is a key test where a tiny piece of tissue, cells, or fluid is taken to be looked at closely in a lab. There are many types of biopsies, and knowing about them is key for patients and doctors.
This article looks at different biopsy procedures, what they’re for, and how they’re done. Plus, it gives info on how doctors figure out what the results mean. About 80% of these tests are done without the need to stay in the hospital. This shows how big a part they play in today’s medicine. There are many ways to get the important tissue samples, from using needles with the help of pictures to more complex surgery.
Learning about the biopsy process and what the findings mean is powerful. It helps patients feel sure as they deal with their health care journey.
Key Takeaways
- Biopsies are key in finding out about diseases, especially cancer.
- Most needle biopsies happen without needing to stay in the hospital.
- There are biopsies for various organs and medical needs.
- Doctors often use imaging to help guide needle biopsies.
- Knowing what biopsy results mean can improve how patients deal with their health.
- Looking closely at the biopsy samples is vital in confirming a diagnosis.
What is a Biopsy?
A biopsy is when doctors take a small piece of tissue or cells from the body. This happens when symptoms suggest there might be health issues. Through knowing about biopsies, we understand these samples are key for diagnosis and planning treatment.
The work of a medical pathologist is very important here. Once a biopsy is done, these samples go to a lab. There, a pathologist checks them to see if there are cancerous cells. This helps decide the treatment path for the patient.
Biopsies can happen in different ways, like using a needle, an endoscope, or through surgery. Each method depends on where and what tissue needs to be looked at. For instance, a stomach biopsy checks for inflammation or bacteria. A lung biopsy helps tell if a lump is cancerous or not.
Thanks to medical progress, biopsies are now safer and easier to do. They usually don’t need you to stay in the hospital. Usually, people recover quickly, and the results come in a few days. This shows how fast diagnosis can help improve health.
Purpose of a Biopsy
The main goal of a biopsy is to check the body’s cells for any serious health issues. It helps doctors see more than just signs of cancer. They can also spot other medical problems by taking a small piece of tissue from the body.
Even though MRIs and ultrasounds can show areas that might be a concern, they can’t tell cancer cells from healthy ones. This is why biopsies are important. By looking at tissue samples under a microscope, doctors can tell if there is cancer.
There are many types of biopsies, like needle biopsies, excisional biopsies, and skin biopsies. Each one is used for different symptoms and parts of the body. They help diagnose conditions like inflammation, infections, and skin problems.
Pathologists are key in looking at the biopsy samples. Their findings help decide on the best treatment. Biopsy results reveal if cancer is present and how severe it is. This helps doctors make a treatment plan and change it if needed.
For those wanting to know more about this important test, visit Mayo Clinic.
Types of Biopsy Procedures
It’s important to know about the different types of biopsies. Many are designed for certain areas and conditions in the body. Each one helps get a clear tissue sample. This helps doctors make the right diagnosis.
Here are the five main kinds of biopsy procedures:
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: Mainly checks for blood diseases like leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
- Needle Biopsy: Includes techniques such as Fine-Needle Aspiration and Core Needle Biopsies. These are used for tumors in tissues.
- Endoscopic Biopsy: Used for getting samples from the bladder, lung, or colon.
- Skin Biopsy: This group has methods like Shave, Punch, Incisional, and Excisional Biopsies. They check skin lesions and possible cancers.
- Surgical Biopsy: Done when other methods can’t reach the area. It allows for deeper access.
Medical imaging is crucial for guiding biopsies. For example, ultrasound helps place needles accurately in breast biopsies. Testing the tissue can tell if cells are cancerous. It also reveals the type and location of the cancer.
Understanding biopsy types and uses helps doctors treat patients better. For detailed info on biopsy methods and their use in cancer care, click the links here and here.
Needle Biopsy Procedures
Needle biopsy procedures use special methods to get tissue samples from areas of concern in the body. They are less invasive, which means less pain for patients. There are different types, like fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, and a few others.
Fine-Needle Aspiration
Fine-needle aspiration uses a thin needle for collecting cells. It’s good for checking lymph nodes and thyroid glands. The process is quick, takes about an hour, and you can go home soon after.
Core Needle Biopsy
A core needle biopsy takes a larger tissue piece, offering more details than fine-needle aspiration. It’s useful for looking at tumors in the breast and liver. This type gives bigger samples, helping to make a clear diagnosis.
Vacuum-Assisted Biopsy
Vacuum-assisted biopsy uses suction to get more samples through one needle entry. It’s especially good for examining bigger lesions in the breast. Fewer needle insertions are needed, which makes the diagnosis more accurate.
Image-Guided Biopsy
Image-guided biopsy uses CT scans or ultrasounds to precisely target areas. It’s great for spots that cannot be felt from the outside. This technique improves the biopsy’s precision. Patients may need to take certain medicines before this biopsy, especially if they’re allergic to contrast materials.
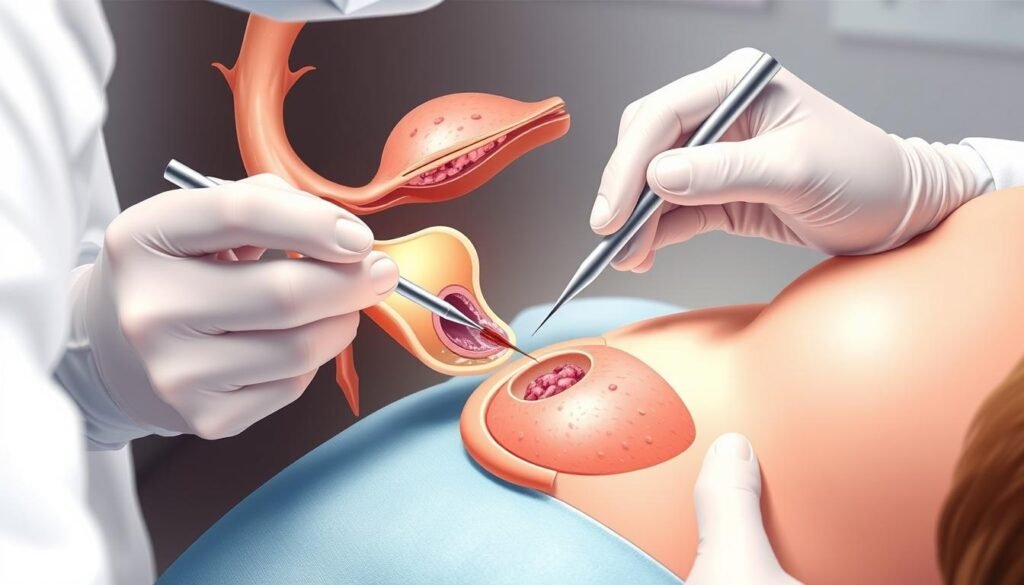
Knowing about these needle biopsy techniques is crucial for those getting tested. Talking with healthcare providers helps understand the benefits and what to expect from each method.
| Biopsy Type | Needle Size | Sample Quality | Recovery Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fine-Needle Aspiration | Thin | Cellular | 1-4 hours observation |
| Core Needle Biopsy | Larger | Histological | 1-4 hours observation |
| Vacuum-Assisted Biopsy | Medium | Multiple samples | 1-4 hours observation |
| Image-Guided Biopsy | Varies | Targeted | 1-4 hours observation |
Endoscopic Biopsy Techniques
Endoscopic biopsy techniques use a camera on a flexible tube to check inside the body and get tissue samples. These methods are not very invasive. They help doctors make accurate diagnoses and patients recover quickly. They target different body parts like the bladder, lungs, and colon.
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy checks the urinary bladder with a thin tube through the urethra. This endoscopic biopsy technique lets doctors see inside the bladder and get samples if they find something wrong. The procedure is usually done with local or general anesthesia. It can find bladder cancer, infections, or swelling. It lasts 15 to 30 minutes, and you’ll recover in about 30 minutes to a few hours.
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy looks at the lungs and breathing paths to find lung diseases. It can spot infections and tumors. In this procedure, a scope goes through the nose or mouth into the lungs. Doctors may take tissue for more tests with an endoscopic biopsy. It takes 30 minutes to an hour. The sedation and recovery are similar to cystoscopy.
Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy checks the colon for digestive issues. This endoscopic biopsy procedure screens for diseases like inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. A scope goes in through the rectum. It can find polyps or odd growths that might need a biopsy. The procedure is 30 minutes to an hour. Recovery from the sedation takes a few hours.
Skin Biopsy Explained
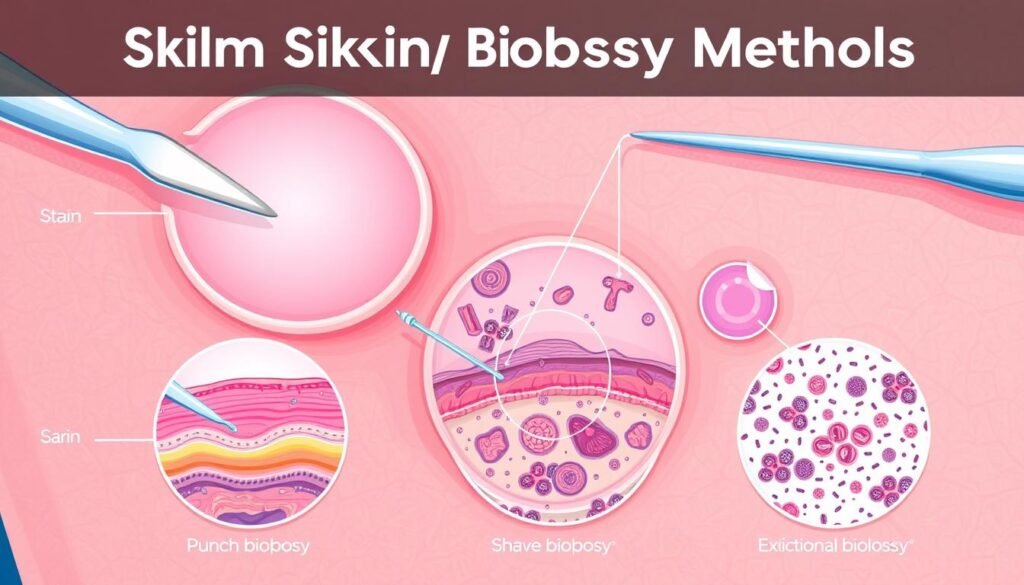
Skin biopsies are key in diagnosing different skin issues, especially skin cancer. Knowing the various types of biopsies helps understand their purposes and how they’re done. Here’s a look at some common biopsy techniques.
Shave Biopsy
A shave biopsy takes off a thin skin layer. It’s usually fast and often doesn’t need stitches, making it a handy choice for removing surface lesions. It’s a good way to check for skin cancer or other problems without affecting deeper tissues.
Punch Biopsy
The punch biopsy removes a skin cylinder for a deeper look. It’s used for checking moles or lesions that need a more thorough examination. Stitches might be required, depending on the sample size.
Incisional Biopsy
An incisional biopsy takes out a bigger skin piece for a deeper analysis. This method is useful when a large sample is needed to examine a suspicious growth. Not the whole area needs to be removed, just a part.
Excisional Biopsy
The excisional biopsy method cuts out an entire suspicious skin area and some healthy tissue around it. This complete removal helps get rid of potential cancer cells. It usually needs stitches. The healing might take longer because it removes more tissue.
| Biopsy Type | Procedure | Stitches Required | Depth of Tissue Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shave Biopsy | Scrapes off the top layer of skin | No | Surface layer only |
| Punch Biopsy | Cylindrical core extraction | May be needed | Deeper layers |
| Incisional Biopsy | Removal of a larger skin portion | May be needed | Deeper tissue |
| Excisional Biopsy | Complete removal of suspicious area | Yes | All layers involved |
Skin biopsies play a vital role in catching and treating skin cancer early on. Knowing the different biopsy options can help you make smart choices about your skin care.
Bone Marrow Biopsy Overview
A bone marrow biopsy is a key step in diagnosing blood cancers and other disorders. It involves taking a sample of bone marrow, the soft part inside bones. This helps doctors see how well the bone marrow is making blood cells.
It’s especially useful when dealing with unexplained anemia. The test looks for problems with red, white blood cells, or platelets. It’s vital in spotting conditions like leukemia or lymphoma. It also checks if cancer has spread to the bone marrow.
Though it’s mostly safe, there are some risks like bruising or discomfort. Rarely, it could lead to serious bleeding or infection. Patients might need to skip eating or drinking before it. They might also get medicine to relax.
After, pain relief might be needed to handle discomfort. Watching for signs like fever or worsening pain is key. The results could take some days but are crucial. They show if blood cells are healthy or if there are signs of disease. A normal result means the marrow’s cell-making process is good. But, abnormal results could suggest serious illnesses.
| Bone Marrow Biopsy Aspects | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Assess blood cell production and diagnose diseases |
| Common Conditions Diagnosed | Anemia, leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma |
| Duration | Approximately 10 to 20 minutes |
| Risks | Bruising, discomfort, rare infections |
| Post-Procedure Care | Monitor for fever; follow bathing instructions |
Surgical Biopsy Procedures
Surgical biopsy procedures are key in getting tissue samples. They help doctors understand medical conditions better. When other sampling methods don’t give clear results, surgical biopsies are needed. In these, a surgeon cuts into the body to reach the concerning area. They either take out the whole lump or just part of it.
There are two main kinds of surgical biopsies: excisional and incisional. Excisional biopsies remove the whole abnormal area. This gives a complete sample for testing, allowing a thorough examination. Incisional biopsies, instead, remove only a piece of the lump. They are not as common as excisional biopsies.
Surgical biopsies are used for issues that can be seen or felt. Sometimes, doctors use imaging like ultrasound, CT scans, or mammography to find the exact spot. Pathologists then study the samples. They look at cell types and check for cancer or other problems.
After a surgical biopsy, patients may have bleeding, bruising, or infection. These side effects show that surgical biopsies are more invasive than other kinds like needle biopsies. Recovery time varies but overnight hospital stays are usually not needed.
For breast biopsies, doctors make sure they know the exact spot before surgery. They examine the tissue closely. They look for cancer, tumor size, and other important details. This helps in planning the best treatment.
In conclusion, surgical biopsies are very important for accurate diagnoses. They help understand body abnormalities well. The information they provide is crucial for treatment and patient care.
Explanation of Biopsy Procedures and Results
A biopsy starts by taking a tissue sample from your body. This sample is then analyzed in a lab. There are many ways to do a biopsy, like needle biopsies and surgery. It depends on where and what needs to be checked. Methods like fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, and vacuum-assisted biopsy are common. Each one tries to get enough tissue for a good look.
After getting the sample, pathologists start examining it. They treat the tissue with chemicals, cut it thinly, and dye it. This makes it easier to see under a microscope. This phase is crucial for understanding the tissue’s health, helping to spot things like cancer or other diseases.
The biopsy results usually come back in a few days. Sometimes, more complex tests take longer. The main goal is to find out what’s wrong, like cancer, infections, or autoimmune diseases. Knowing how biopsies work can help patients know what to expect.
Pathology Analysis and Diagnosis Confirmation
Pathology analysis is key in confirming diagnoses, especially with cancer. Doctors take tissue samples and look at them closely. They search for cancer cells and figure out the cancer’s type and severity. This info helps doctors plan treatment and predict the patient’s outlook.
The pathology report contains important details like the patient’s name and the biopsy date. It also has a sample id and tells us about the biopsy’s look and feel. For big samples, it lists tumor size and if it has spread to lymph nodes.
The report’s microscopic section is super important. It describes cancer cells’ looks and arrangement. It talks about tumor grading on a scale from 1 to 4. A higher grade means the cancer is more aggressive and might need stronger treatment.
Sometimes, biopsy results aren’t clear, so more tests are needed. The College of American Pathologists sets rules to help give accurate diagnoses. They ensure every case is handled correctly.
Usually, doctors get the pathology report within 10 days after the biopsy. If it’s urgent, like during surgery, pathologists can give a quick preview in about 15 to 20 minutes. This quick feedback can help make fast treatment choices.
Now, pathology tests often include molecular tests to better define the cancer type and treatment options. These advanced tests provide vital details for patient care and are added to the pathology reports.

Post-Procedure Care for Patients
Caring after a biopsy is key to a good recovery. Patients might feel slight pain, swelling, or bruising. Handling these can make recovery better. Doctors give clear instructions for the recovery time.
Managing Side Effects
Watching for changes after a biopsy is important. For pain, patients can use medicines from the store. A waterproof bandage helps prevent infection for a day. Avoid hard activities to help healing.
Doctors check the healing 7 to 10 days later. If there’s a fever, big pain, or lots of redness, call a doctor right away. Watching these signs helps avoid problems and aids healing.
| Side Effect | Management | Follow-Up |
|---|---|---|
| Localized Pain | Over-the-counter pain relief | Follow-up appointment in 7-10 days |
| Swelling | Rest and ice application | Sutures removal if applicable |
| Bruising | Monitor and avoid straining the area | Consult if symptoms worsen |
| Severe Reactions | Immediate contact with a physician | N/A |
These care tips can make recovery easier. Being informed makes this important time safer and more comfortable.
Understanding Biopsy Results
Getting your biopsy results means learning about the language in the pathology report. Pathologists look at these samples closely to help take care of you. They use the report to share what they find about different cells and health issues.
Patients often see medical terms in their reports. For breast, you might see words like breast carcinoma, lobular carcinoma, or atypical hyperplasia. For the colon, terms might include sessile or serrated polyps. These terms help doctors decide if you need more treatment or checks.
Those with esophagus biopsy reports might see terms like carcinoma or Barrett’s esophagus mentioned. Lung reports may talk about non-cancer issues such as granulomas or inflammation. They can also mention cancer types. Understanding these words is key to knowing what your report says about your health.
Learning about your biopsy results is important. Talking with your doctor about any questions helps you understand better. If you’re not sure about the findings, it’s okay to ask another doctor for their opinion. This helps you feel sure about your health information.
| Type of Biopsy | Common Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Breast Biopsy | Breast carcinoma, atypical hyperplasia | Possible need for further treatment or monitoring |
| Colon Biopsy | Colon polyps, colon cancer | Increased risk assessment and management strategies |
| Esophagus Biopsy | Carcinoma, Barrett’s esophagus | Potential surgical intervention or surveillance |
| Lung Biopsy | Granulomas, cancer type | Guidance on treatment options based on findings |
| Bone Marrow Biopsy | Leukemia, lymphoma | Critical for diagnosing hematologic conditions |
Following up after a biopsy is very important. It gives you a chance to go over the results with your doctor and plan treatments. It keeps you in the loop about your care.
Conclusion
Biopsies are key in diagnosing and identifying conditions like cancer. They come in different forms, like needle biopsies and imaging-guided ones. Each method has a special role in diagnosing and caring for patients.
Good healthcare starts with doctors and patients talking clearly about biopsies. Lab analyses of the samples are critical for choosing the right treatment. Understanding every step helps patients and leads to faster treatment when needed.
Knowing about your biopsy helps you be part of your healthcare. Talking with your doctors lets you help in making decisions. This teamwork improves your health outcomes and awareness.