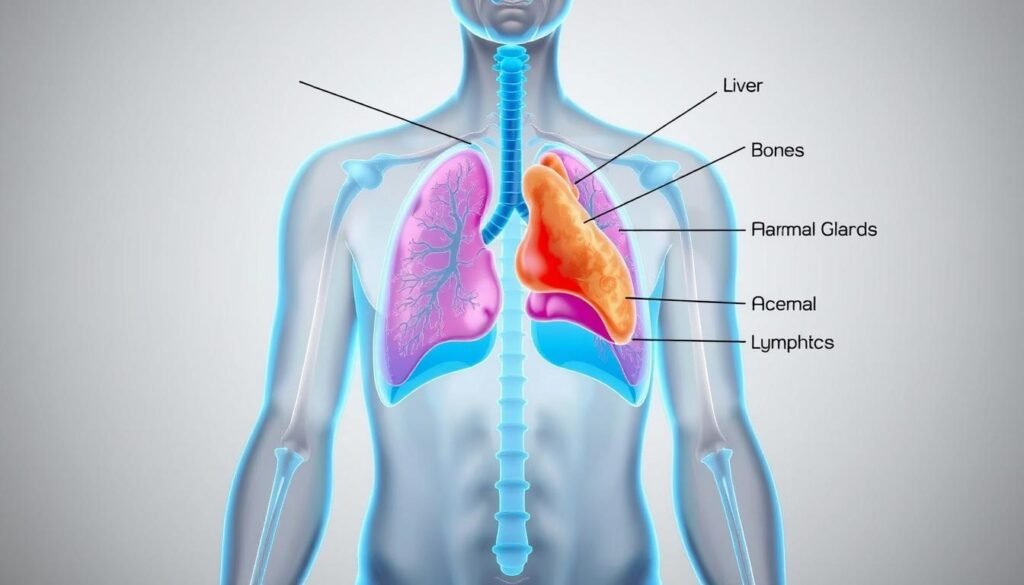
About 40% of people who find out they have lung cancer learn it has spread. This condition is called advanced lung cancer. It’s important because it changes how doctors treat the patient and their chances of getting better. The most common places it spreads to are the lymph nodes, the brain, the bones, the liver, and the adrenal glands. Knowing where the cancer might go helps doctors create the best plan for their patients.
Key Takeaways
- Metastasis occurs in about 40% of people newly diagnosed with lung cancer.
- The brain, bones, liver, and nearby lymph nodes are common sites of lung cancer metastasis.
- Understanding these sites is crucial for effective treatment and management strategies.
- Advanced lung cancer includes locally advanced cases with significant spread to surrounding tissues.
- Survival rates for metastatic lung cancer can be as low as 6.3% over five years.
Understanding Lung Cancer Metastasis
Lung cancer metastasis is a key concern in treating this illness. Cancer cells may leave the original tumor and travel. They use the bloodstream or lymphatic system to reach new organs. About 40% of people with lung cancer will see it spread.
It’s crucial to know the difference between local and metastatic lung cancer. Local cancer usually affects nearby lymph nodes. Metastatic cancer, however, spreads to distant organs. Most lung cancers are found at stage IV, meaning they have already spread.
Lung cancer spreads in several ways. For early-stage tumors, blood vessel invasion increases the chances of the cancer coming back. This reduces patient survival. The brain, bones, and adrenal glands are common places for spread. Small cell lung cancer often moves to the liver.
To diagnose metastatic lung cancer, doctors do tests like bronchoscopy and chest scans. Treating it depends on where it has spread. Knowing these patterns helps improve patient outcomes. Looking closely at stage IV lung cancer offers insight into treatments and care. This aims to better the lives of patients.
| Metastatic Site | Common Types of Lung Cancer | Impact on Survival |
|---|---|---|
| Brain | Adenocarcinoma, SCLC | Increases complications, worsens prognosis |
| Bones | All types | Can lead to severe pain and mobility issues |
| Liver | SCLC | Common site with poor prognosis |
| Adrenal Glands | All types | May require targeted therapies |
Common Lung Cancer Metastasis Sites
Lung cancer can spread to key areas in the body. Knowing where it spreads helps doctors diagnose and manage it. This part talks about the main places lung cancer goes to. It looks at why these places are important when lung cancer spreads.
The Brain
About 47% of people with lung cancer will find it spreads to their brains. This can cause big health problems like bad headaches, confusion, and seizures. Finding it early is key to treat these issues well.
The Bones
In 30% to 40% of lung cancer cases that are advanced, the cancer moves to the bones. This leads to a lot of pain or bones breaking because they get weak. Knowing these common spread sites helps doctors manage pain better.
The Liver
The liver might be affected in 30% to 50% of people with lung cancer. They might feel very tired, get jaundice, or feel generally unwell. It’s important to keep an eye on liver health in these patients.
The Adrenal Glands
Adrenal gland metastasis often doesn’t show symptoms. Even without symptoms, it impacts health a lot. Regular checks are a must for lung cancer patients.
Nearby Lymph Nodes
Cancer cells often move to lymph nodes close to the lungs. This shows the disease might spread more. Knowing this helps doctors make better treatment plans.
| Site of Metastasis | Prevalence (%) | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Brain | 47% | Headaches, confusion, seizures |
| Bones | 30% – 40% | Severe pain, fractures |
| Liver | 30% – 50% | Fatigue, jaundice |
| Adrenal Glands | 15% | Often asymptomatic |
| Nearby Lymph Nodes | Variable | May indicate further spread |
Lung Cancer Spread Mechanisms
Understanding how lung cancer spreads is key to managing it. Cancer cells move through blood or lymph systems. The blood path is called hematogenous metastasis. The lymph path usually hits local lymph nodes first before going farther.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) makes up about 15% of lung cancers. Sadly, almost 70% of these patients have cancer that has already spread when they find out they’re sick. This shows why it’s vital to know how lung cancer spreads early on.
Common places SCLC travels to include:
- Lymph Nodes
- Brain
- Liver
- Bones
SCLC can spread easily because of how tumors act, like having leaky blood vessels. High numbers of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in SCLC patients link to how advanced the cancer is and survival chances. This means watching CTC levels can help figure out how the patient might do.
New methods focus on certain steps of tumor growth. For instance, how vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) and hypoxia inducible factors (HIF) interact during cancer spread. Treatments aiming to change the body’s immune response look promising. They could improve how we tackle lung cancer spread.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer Metastasis
It’s key to know the symptoms of lung cancer metastasis for early treatment. These symptoms often change depending on where the cancer has spread. Usually, there are common signs that show cancer might have spread in the body.
General Symptoms Associated with Metastasis
Some usual symptoms of lung cancer spread include:
- Unexplained weight loss: This often indicates changes in how the body uses energy.
- Fatigue: This means feeling very tired, making it hard to do everyday tasks.
- Pain: This can feel different in intensity and happen in many places.
Site-Specific Symptoms
Where the cancer spreads can change the symptoms you might have:
| Site | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Brain | Drowsiness, confusion, bad headaches, weakness in arms or legs. |
| Bones | Intense pain, weak legs, numbness, trouble with bladder or bowels. |
| Liver | Pain on the right side of the belly, yellow skin, weight loss, fluid in the abdomen, skin itch. |
| Adrenal Glands | Feeling dizzy or weak, very tired, weight loss without trying. |
| Lymph Nodes | Swollen or lumpy areas in the neck or underarms. |
Knowing these signs of lung cancer spread is crucial. It helps get the right treatment early, which can lead to better health results.
Lung Cancer Metastasis Sites: Prognosis and Survival Rates
Lung cancer spreading is very serious. The five-year survival rate is about 18.6%, showing the big hurdles patients face. Survival rates vary greatly between non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Knowing these differences helps patients and families know what to expect.
Understanding Survival Rates for Metastatic Lung Cancer
Survival rates for metastatic lung cancer vary a lot. For instance, the five-year rate for small cell lung cancer is around 3%. For non-small cell lung cancer, it’s a bit better at 8%. Sadly, 25-30% of those with advanced NSCLC may live less than three months. Survival greatly depends on how far the cancer has spread:
| Stage | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|
| Localized NSCLC | 65% |
| Regional NSCLC | 37% |
| Distant NSCLC | 9% |
| Localized SCLC | 30% |
| Regional SCLC | 18% |
| Distant SCLC | 3% |
The stage of the cancer drastically affects survival rates. Early stages like localized and regional have higher survival rates. However, once the disease is advanced, chances for long-term survival drop sharply.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
A few factors influence lung cancer’s outlook. Age, health, and where the cancer has spread affect survival. Patients with cancer in the lungs do better than those with it in the liver, which has very low survival rates. Also, race affects survival, with Black individuals having higher death rates from lung cancer. This shows the need for treatments tailored to each patient’s unique situation.
For more on how different metastasis sites affect prognosis, check out this comprehensive study here.
Treatment Options for Lung Cancer Metastasis
When dealing with lung cancer metastasis, treatment mainly helps manage symptoms. It aims to improve patients’ quality of life. These treatments include various therapies suited for the disease’s different stages.
Overview of Treatment Modalities
Treatment for metastatic lung cancer often combines several approaches:
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Radiation therapy
Doctors use a team approach to create customized treatments for lung cancer metastasis. This is especially true for advanced cases, like non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). These treatments help manage symptoms and give patients hope. Knowing about specific genetic markers helps choose the best therapy. For more on treatment options, visit this link.
Palliative Care Strategies
Palliative care is crucial for those with advanced lung cancer. It focuses on relieving symptoms like pain and breathlessness. Common tactics include:
- Emotional support through counseling and support groups
- Hiring professional caregivers for assistance
- Support from family and friends
- Preparing for end-of-life care, including hospice services
Also, getting financial and legal affairs in order gives patients and families peace of mind. Discussing treatment preferences ensures care respects patients’ wishes. Support networks help lighten the emotional load of lung cancer metastasis treatment.
Risk Factors for Lung Cancer Metastasis
It’s crucial to know about lung cancer metastasis risk factors. This helps in spotting the disease early. Many factors can influence the chance of lung cancer developing. It can also affect how it spreads in the body.
Genetic Factors
Genetic predispositions play a big role. If your family has a history of lung cancer, your risk may be higher. This family history affects how lung cells deal with harmful substances. It makes them more likely to turn into cancer. Also, certain genetic mutations help cancer cells grow. They help cancer cells spread to places like the bones and brain.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors are key too. For example, tobacco smoke causes about 80% of lung cancer deaths in the US. Being around radon gas is the second leading cause of lung cancer. Working with asbestos or being in polluted air also raises your risk. It’s important to avoid these risks to lower your chances of getting lung cancer.
A healthier lifestyle helps reduce your risk. Quit smoking and eat more fruits and vegetables. For more tips on spotting lung cancer signs, check out this guide.
Managing Lung Cancer Metastasis
Managing lung cancer spread means a tailored plan for each patient. It involves symptom relief, coordinating therapies, and working with care teams. Treatments like chemotherapy or radiation play a big role when surgery isn’t an option. Technologies like PET and CT scans are key for finding where the cancer has spread.
Clinical Management Approaches
Doctors use different methods to help lung cancer patients. They might use radiation to ease symptoms and help patients breathe easier. Newer treatments like stereotactic body radiation and CyberKnife pinpoint cancer more accurately. Places like Fox Chase Cancer Center are testing new ways based on cancer origin to enhance outcomes.
Importance of Supportive Care
Supportive care is vital in handling lung cancer’s spread. It helps patients feel better emotionally and mentally during treatment. Techniques like stent insertion and brachytherapy help manage symptoms, improving life quality. This care works alongside clinical treatments, helping patients cope better.
Patients with symptoms like coughing and bleeding should get help right away. Early help can manage serious conditions, as noted on lung health awareness platforms.