Did you know small cell lung cancer (SCLC) makes up about 15% of all lung cancer cases in the U.S.? It mainly targets people who have smoked and grows and spreads quickly. For those dealing with SCLC, understanding its details is key to managing treatment.
This guide will cover the basics of small cell lung cancer, including what it is, the symptoms, how it’s diagnosed, treatment paths, and where to find support. Knowing these things can help ease the stress of a cancer diagnosis. For those looking for more details on treatments, the American Cancer Society has a wealth of information.
Key Takeaways
- SCLC represents about 15% of all lung cancers, primarily affecting smokers.
- Common treatment modalities include chemotherapy, radiation, and emerging immunotherapies.
- SCLC can be classified into limited-stage and extensive-stage disease, influencing treatment decisions.
- Diagnostic tests like imaging and biopsies play crucial roles in SCLC cancer diagnosis.
- Support resources are available through advocacy groups and cancer support networks.
What is Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)?
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) is a fast and severe lung cancer type. It starts in the bronchi with small, oval cells that grow quickly. It’s known as a neuroendocrine tumor and is more common in people who smoke a lot. Definition of SCLC is crucial as it makes up about 15% of lung cancers. Each year, it causes around 250,000 new cases and 200,000 deaths globally.
Definition and Overview
SCLC stands out because it grows fast and spreads early. Often, it’s already in an advanced stage when found. Smokers are mostly at risk, with only 2% of cases in non-smokers.
Patients usually also have COPD, making their health worse.
Difference Between SCLC and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
SCLC and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are not the same. They grow differently and need different treatments. SCLC spreads more quickly. Thus, it needs stronger treatment.
People with early SCLC might live 18 to 23 months. Those with advanced SCLC live about 8 to 10 months. Early diagnosis can sometimes lead to long-term survival. For more details, check the definition of SCLC.
SCLC Symptoms
Spotting small cell lung cancer (SCLC) symptoms early can make a big difference. It helps get treatment started sooner. Here are the main symptoms of SCLC.
Common Symptoms of SCLC
At first, SCLC might not show clear signs. But as it grows, certain common symptoms of lung cancer appear:
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Coughing up blood or mucus
- Unexplained weight loss
These SCLC symptoms often start because the tumor affects nearby tissues and organs. This can impact breathing and overall health.
Signs That May Indicate Advanced Disease
When SCLC gets worse, new advanced SCLC signs may show up. Look out for these:
- Severe chest pain
- Difficulty swallowing
- Swelling in the face or neck
- Neurological symptoms like headaches or seizures
Noticing these advanced signs is key. They could mean you need quick care from a doctor.
| Symptom | Stage | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Persistent cough | Early | Often minimal at first |
| Chest pain | Early to Advanced | May worsen as disease progresses |
| Shortness of breath | Early to Advanced | Fluid buildup in lungs |
| Coughing up blood | Advanced | Indicates significant tumor impact |
| Unexplained weight loss | Advanced | Weight loss common in various cancers |
| Difficulty swallowing | Advanced | May indicate tumor pressure |
| Neurological symptoms | Advanced | Can signal spread to nervous system |
SCLC Diagnosis
Doctors start diagnosing small cell lung cancer because it spreads fast. They look for symptoms or unusual signs in tests. They use different tests to find and understand the disease fully.
Diagnostic Tests for SCLC
Doctors use tests like X-rays and CT scans. The Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center uses special scans with less radiation. Biopsies are important for confirming cancer. Various biopsy methods are chosen based on the patient’s needs. They help identify the cancer type and stage.
The Role of Imaging and Biopsies
Imaging shows where cancer is and how far it has spread. PET scans and nuclear imaging help see if the cancer is in early or late stage. Biopsies are key for diagnosis and treatment planning. Accurate diagnoses lead to better treatment picks. Most SCLC patients have advanced disease at diagnosis. Good imaging and biopsies guide the treatment plan. For more on SCLC research, click here.
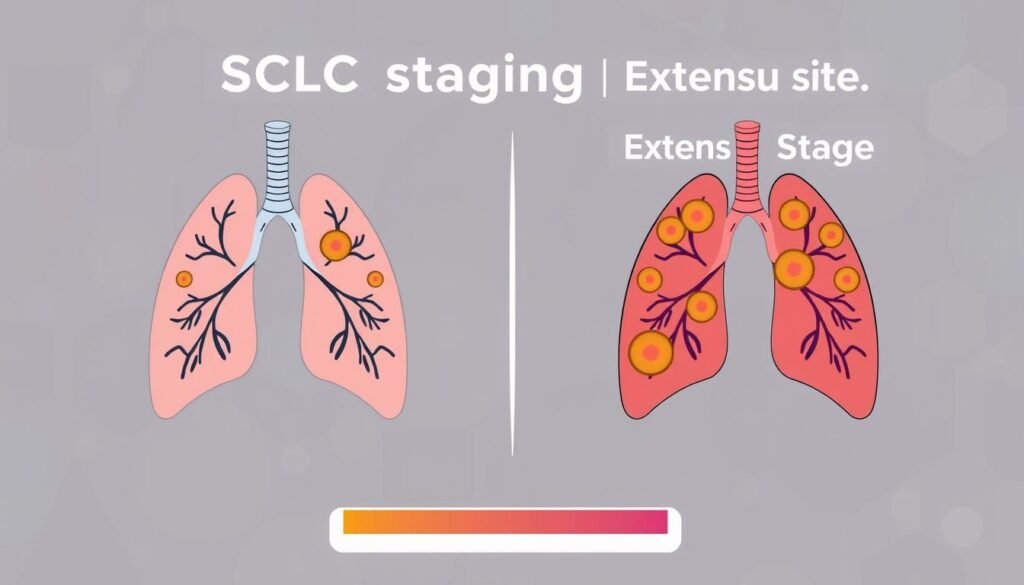
SCLC Staging
SCLC is mainly put into two stages: limited and extensive. Knowing the stage is important for choosing the right treatment. About 1 in 3 people with SCLC have the limited stage. The others have the extensive stage.
Understanding Limited Stage vs. Extensive Stage
Limited stage SCLC is in one lung and maybe nearby nodes. This allows for stronger treatments like chemo and radiation to try to cure it. Extensive stage SCLC means the cancer is more widespread. Here, the focus often shifts towards easing symptoms.
The TNM system is also used. “T” is for tumor size, “N” is for node involvement, and “M” is for metastasis.
Importance of Staging in Treatment Planning
Knowing the SCLC stage helps doctors choose the best treatment. Limited stage often leads to chemo and radiation together. Extensive stage mainly needs treatments to relieve symptoms. For both stages, understanding the importance of staging helps create personalized treatment plans.
| Stage | Description | Typical Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Stage | Cancer confined to one lung and nearby lymph nodes. | Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy |
| Extensive Stage | Cancer has spread to other areas beyond the lung. | Palliative Care, Symptom Management |
SCLC Treatment Options
Treating Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) means looking at many options. This cancer is aggressive. So, doctors use many treatments together to help patients.
Standard Treatment Approaches
Chemotherapy and radiation are key for SCLC. Chemotherapy is the main treatment. Radiation helps control the cancer in one area. When the cancer hasn’t spread much, doctors combine these treatments to make them better. Sometimes surgery is possible, but not often.
Emerging Treatment Methods
New treatments like immunotherapy are being tested. They show promise in helping some patients. It’s a good idea to talk about these new options with doctors. They might work well with traditional treatments.
The Role of Clinical Trials in SCLC Treatment
Clinical trials are very important. They test new treatments. Patients in trials can get new therapies not widely available yet. This helps everyone learn more about SCLC. If you have SCLC, ask your doctor about trials. For more about treatments, click here.
SCLC Prognosis
The outlook for Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) is complex. Many factors play a big role in the outcomes. Knowing how these factors interact helps patients make treatment choices.
Factors Affecting Prognosis
Several things affect the outlook for SCLC. Important factors include:
- Stage at Diagnosis: Being diagnosed at an early stage usually means a better outlook than at a late stage.
- Patient Health Status: Good health and fewer other illnesses help with better treatment results and survival.
- Response to Treatment: People who respond well to chemotherapy or immunotherapy often live longer.
- Genetic Variations: Certain genetic changes, like YAP1 variants, may lead to longer survival.
Understanding Survival Rates and Statistics
Survival rates for SCLC pose a challenge. This cancer makes up about 15% of all lung cancer cases and mainly strikes smokers. The five-year survival rates are low, highlighting the cancer’s aggressive nature. Yet, progress in treatments and early detection is raising hope.
Even though many patients pass away within five years of being diagnosed, new treatments can extend life for over a year, even with widespread disease. These advances might greatly improve the outlook for SCLC.
Managing Side Effects of SCLC Treatment
People with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) often deal with treatment side effects. Knowing how to handle these symptoms can make life better during treatment. Treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy have unique side effects, needing their own ways to manage.
Common Side Effects of Chemotherapy, Radiation and Immunotherapy
Chemotherapy is a key treatment for SCLC. Side effects often felt include:
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Hair loss
Those getting radiation may face:
- Skin reactions like sunburn
- More tiredness
People on immunotherapy might have:
- Flu-like signs
- Nausea
- Skin rashes
It’s key for patients to talk about possible side effects with their doctors before starting treatment. This ensures they are ready and supported.
Strategies for Side Effect Management
Controlling cancer treatment side effects usually involves different tactics. Here are some helpful ways to ease symptoms:
- Always keep in touch with your healthcare team about your symptoms and worries.
- Use calming methods like deep breathing and meditation to lessen stress and worry.
- Eat small, healthy meals and drink plenty of water to fight nausea.
- Do light physical activities, if you can, to help with tiredness.
- Talk to your healthcare team about extra support, like counseling or rehab.
These methods can hugely help improve treatment experience and patient happiness.
Support Resources for SCLC Patients
Finding out you have Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) can feel really tough. Getting the right support is crucial. There are many groups and services ready to help with both information and emotional backing for patients and their families.
Educational Resources and Advocacy Groups
There are lots of groups dedicated to SCLC that offer vital info and support. LUNGevity and the American Cancer Society provide resources to understand the illness and treatment better. They also offer spaces for patient discussion. This boosts engagement in their care and builds community among those dealing with SCLC.
Cancer Support Networks and Counseling
Cancer support networks offer essential emotional backing for patients and their families. Meeting others in similar situations can bring much-needed comfort. There are counselors ready to help deal with the emotional toll. These services support both patients and those taking care of them. They offer a space to talk about worries and guide families on their journey.
Conclusion
It’s vital to understand Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) if it affects you or someone you know. It makes up a small part of lung cancers but grows quickly and can greatly lower survival rates. Knowing about SCLC helps patients and their families face the disease.
Even though SCLC’s outlook seems grim, research is leading to new hope. Innovative treatments, like immunotherapy and DNA agents, are being explored. This shows why it’s key for patients to know about their care options and talk to their doctors.
Strong support is key for those battling SCLC. Joining support networks helps with emotional strength and provides helpful resources. Working with support groups and doctors can make dealing with SCLC’s challenges easier.