Did you know nearly 90% of all deaths from cancer are due to its spread? This fact highlights the need to grasp how cancer can move through the body. Metastasis means cancer cells leave their original spot and form new tumors elsewhere. This shows cancer has reached a serious level. This can deeply affect patients and their families mentally and physically.
This piece sheds light on metastatic cancer. It explains what it is, how it happens, and where it often spreads. Also, it discusses symptoms, how to diagnose it, and what treatments are available. Knowing more helps patients and their families deal with cancer’s complexities better. For more info, check out the details of metastatic cancer.
Key Takeaways
- Metastatic cancer is cancer that has moved from its first place to other body parts.
- It involves invading nearby tissues and spreading via lymph nodes or blood vessels.
- Metastasis often happens in bones, liver, and lungs, causing different symptoms.
- Treating metastatic cancer aims to slow its growth and make symptoms less severe.
- Knowing cancer stages is key to choosing the right treatment.
What is Metastasis?
Metastasis is when cancer cells leave the main tumor and spread to other body parts. They travel through blood or lymph systems and form new tumors elsewhere. This is how cancer spreads and gets worse. When cancer moves like this, it is called stage IV cancer. Yet, it keeps the name of the original cancer, like metastatic breast cancer in the lungs.
Most cancer deaths, about 90%, happen because of this spread. Around 1 in 3 people in the U.S. will face cancer. Both types of tumors, fast and slow growing, can spread. But how they do it and the secondary cancers they make can differ. Unlike benign tumors, malignant ones can invade nearby areas and spread through blood, leading to metastasis.
Many factors play a role in cancer spreading. These include genetics, life choices, and environment. The cancer stage is key in deciding how to treat it and what to expect. By understanding how cancer spreads, we can find better ways to manage it. This can lead to better care and outcomes for patients.
How Metastasis Occurs
The journey of metastasis begins when cancer cells move from their original location. They start by invading nearby tissues. This is crucial for the cells, as they adapt to survive harsh conditions. Once past the local barriers, they can travel via blood or lymph systems.
Next, they enter the circulatory system and move until they reach distant organs. Here, many cells die, but a few manage to survive and face more challenges. These surviving cells then try to grow in new areas. They need blood vessels to support their growth and form new tumors.
It’s interesting that less than 1 out of 10,000 cancer cells can form new tumors. This shows how complex and selective the process is. Different cancers spread to specific places first. For instance, breast and prostate cancers usually move to bones first. Lung cancer often goes to the adrenal glands. A chemokine called CXCL12 plays a role in guiding these cells.
Understanding how metastasis works is key to cancer research. Scientists are looking into the genetic factors involved. This could help find new treatments. Sadly, metastasis is the main reason cancer is so deadly, causing over 90% of deaths. The process is complicated, with many steps that challenge researchers to find effective treatments.
Common Sites of Metastasis in Various Cancers
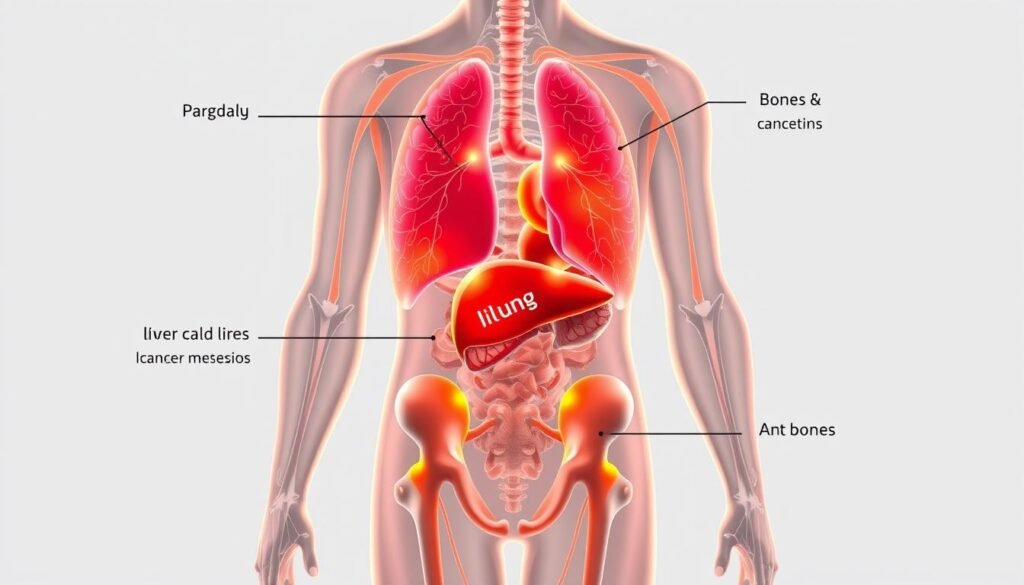
Understanding where cancer commonly spreads helps doctors plan treatments better. Certain organs are more likely to be affected by cancer spread. The bones, liver, lungs, and brain are often where metastasis occurs.
For example, breast cancer tends to spread to the bones, brain, liver, and lungs. Prostate cancer, on the other hand, often moves to the bones and liver.
Colorectal cancer usually makes its way to the liver. This is a key focus for those in healthcare. Testicular cancer often moves to the lungs. Ovarian cancer is known to reach the peritoneum.
The spreading of cancer can be seen as local, regional, or distant. Metastatic cancer means it has spread far, like to distant organs or lymph nodes.
Doctors need a deep understanding of these spreading patterns. This knowledge helps them make better treatment plans. They can foresee and deal with complications from metastasis, improving patient care.
| Cancer Type | Common Metastasis Sites |
|---|---|
| Breast Cancer | Bones, Brain, Liver, Lungs |
| Prostate Cancer | Bones, Liver |
| Colorectal Cancer | Liver |
| Testicular Cancer | Lungs |
| Ovarian Cancer | Peritoneum |
Symptoms of Metastatic Cancer
Metastatic cancer symptoms can differ a lot. They depend on how big the tumor is and where it is. Some people might not feel sick at all. But, others can have big health problems. Bone pain, fractures, and sometimes nerve issues are common if cancer spreads to the bones. If it reaches the brain, people might get headaches, seizures, feel dizzy, or not think clearly. When it affects the lungs, they might cough a lot, feel out of breath, and have chest pain.
Liver metastases can cause jaundice, itchy skin, belly swelling, or changes in stool color. Many patients feel a mix of symptoms. These can make life harder. Knowing these signs early helps find the problem faster. This can make treatments work better and help with managing symptoms of cancer.
By knowing the unique signs of cancer, patients and doctors can act fast. Handling metastatic cancer symptoms is tough. But, getting to know about them is the first step in taking control.

| Type of Metastasis | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Bone | Bone pain, fractures, weakness in limbs, urinary and bowel incontinence |
| Brain | Headaches, seizures, mental changes, numbness |
| Lung | Chronic cough, shortness of breath, chest pain |
| Liver | Jaundice, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea |
The Development of Metastasis and Its Symptoms
It is essential to understand how tumors develop. It shows us how cancer spreads. First, cancer cells leave the original tumor. Next, these cells enter nearby tissues and start new tumors. These new tumors need blood to grow and survive. This is called angiogenesis. Studying these steps helps us find new treatments.
Understanding Tumor Formation
Forming tumors in metastatic cancer is not simple. Many types of cells are involved. This includes cells that make up blood vessels and immune cells. Cancer cells can change their surroundings. This lets them grow in new places. The study of exosome vesicles and changes in genes is key. It helps cancer spread. Scientists are working to learn more. This could help stop cancer from spreading.
How Location Affects Symptoms
Symptoms differ depending on where the cancer has spread. Cancer in bones causes pain and could lead to broken bones. But cancer in the lungs might make one cough a lot or have trouble breathing. Knowing these differences helps doctors treat cancer better. Some people might not show any signs of spread. This is why regular checks are very important, especially for those at high risk.
Also, research is looking into how allergies could affect lung cancer. It’s a new area to explore. For more details, you can visit this resource. And you can find out how allergies and lung cancer are linked here.
Diagnosis of Metastatic Cancer
Diagnosing metastatic cancer starts with detailed testing, like cancer testing protocols. First steps include checking the patient’s health history and physical exams. Tests such as blood counts, kidney and liver tests, and scans of the chest and belly are done.
When initial tests don’t find the main tumor, more specific tests are needed. About 76% of primary tumors are found early on. The success of later tests varies, showing why understanding test effectiveness is key.
Biopsies help confirm the type and source of tumors, guiding the treatment plan. The first round of tests finds tumors in 62% of cases. Later tests find them less often, highlighting the importance of early testing.
Imaging is vital for spotting cancer’s spread. Tests tailored for men and women, like mammograms and PSA tests, help find cancer early. This ensures tests match the patient’s symptoms, leading to quick and right diagnoses.
New research underlines how the TNM staging system, assessing tumor size and spread, boosts diagnosis accuracy. This approach, along with advanced imaging, aims for a precise diagnosis to best decide treatment options for metastatic cancer.
| Type of Test | Diagnostic Yield (%) |
|---|---|
| Initial Tests | 62 |
| Additional Tests | 29 |
| Exhaustive Tests | 22 |
| Basic Tests for Primary Tumors | 76 |
Treatment Options for Metastatic Cancer
Treatment for metastatic cancer has different options based on what you need. These options include systemic therapy and localized interventions. It’s important to know the difference between them for managing cancer well.
Systemic vs. Local Therapies
Systemic therapy uses medications to reach cancer cells all over the body. It includes chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy. These treatments help shrink tumors and slow their growth. On the other hand, localized interventions target specific areas. They use surgery or radiation for isolated cancer spots. The choice of treatment depends on the cancer type, how far it has spread, the patient’s health, treatment history, and the cancer’s genetic traits.
- Type and origin of cancer
- Extent of spread
- Patient’s overall health and treatment history
- Genetic characteristics of the cancer
Palliative Care and Quality of Life
Palliative care is key for those with metastatic cancer. It aims to improve life quality by tackling physical, emotional, and psychological needs. This care helps manage pain and discomfort. It’s beneficial along with other treatments to prolong life. Studies show that palliative care *can lead to better quality of life*. It offers comfort and support when it’s most needed.
With better treatment and palliative care approaches, patients can face cancer with dignity. This highlights the importance of care tailored to each person in their cancer journey.
Living with Metastatic Cancer
Living with metastatic cancer is tough. It brings emotional and psychological challenges that need quick attention. Support options like counseling, support groups, and online spaces are very helpful. They let people share stories, find strength, and get encouragement from others in similar situations.
Coping Mechanisms and Support Resources
Good coping methods make people more resilient and improve mental health. These methods can be practicing mindfulness, staying active, and journaling. People often feel better in support groups. They get useful advice from others who understand what it’s like to live with metastatic cancer. This can make them feel normal and included, which really helps their life.
Importance of Clinical Trials
Cancer clinical trials are super important. They help learn more and find treatments for metastatic cancer. Being part of these studies can give patients access to new therapies not yet available to everyone. Trials focus on new treatments and see how patients do over time. This helps find out if treatments work well and how they help patients live longer. Being in trials is a way to help move cancer research forward, helping now and in the future.
| Coping Strategies | Support Resources | Clinical Trials Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Mindfulness practices | Support groups | Access to new therapies |
| Regular physical activity | Counseling sessions | Contributes to research studies |
| Journaling | Online communities | Improves treatment understanding |
People with metastatic cancer can really thrive by using the right coping methods and support. They can also look into clinical trials. This can make a big difference in their care. For more info, visit this resource.
Conclusion
Understanding how cancer spreads and its signs is key to better cancer care. Currently, more than 90% of cancer deaths globally are due to metastasis. This stage affects 10-15% of cancer patients. Yet, from 1991 to 2019, cancer deaths in the U.S. dropped by 32%. This drop is thanks to better early detection, targeted treatments, and preventive steps that help patients live longer.
Knowing about metastatic cancer is vital for cancer awareness and spotting symptoms early. While 5 to 30% of patients survive more than five years, they still need a lot of support. Even as some cancer death rates don’t change much, like in pancreatic and liver cancer, it’s still possible for patients to have quality lives. They can achieve this with care focused on improving life’s quality.
Improving cancer care means always learning about how to catch it early and the treatments for advanced cancer. By spreading the word, we help more people and their families get the help they need fast. This leads to better chances for those dealing with advanced cancer.