Lung cancer is the top cause of cancer-related deaths globally. It kills more people each year than breast, colon, and prostate cancer combined. Both men and women are at higher risk due to factors like smoking and the environment. Knowing about lung cancer is key for early detection and finding the right treatments.
We’ll explore lung cancer affecting both lungs, looking at types, causes, risk factors, and symptoms. We’ll talk about how to diagnose it and the treatments available, such as surgery and chemotherapy. A big fact to remember is that smoking causes 90% of these cases, highlighting the need for prevention.
Dealing with lung cancer also means managing side effects to better the lives of those impacted. For more info, see this detailed guide on treating lung cancer. It gives a good overview of symptoms and how to manage them.
The article also discusses how lifestyle changes and prevention can lower the risk of this serious disease. With ongoing research, understanding and fighting lung cancer is becoming more effective every day.
Key Takeaways
- Lung cancer is the deadliest type of cancer, with the highest annual death toll.
- Smoking is responsible for about 90% of lung cancer cases.
- Secondhand smoke exposure significantly increases lung cancer risk.
- There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer.
- Prevention strategies, including smoking cessation and reducing exposure to carcinogens, are critical.
- Early detection of lung cancer through screening can improve treatment outcomes.
- For extensive information on lung cancer, visit this resource on understanding the disease.
What is Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer starts when cells in the lungs grow out of control. These changes mostly happen in the tissues lining the airways. Because these abnormal cells keep growing, they can form tumors. These harmful tumors can spread and damage healthy tissue. Lung cancer is a leading cause of death worldwide, so knowing about it is crucial for health.
Often, lung cancer is found late, when it’s hard to treat. Catching it early can really improve chances of survival. Doctors might use a tool called a bronchoscope to look at the lungs. This helps them find and check any unusual growths in the airways.
In the UK, smoking causes most lung cancer cases, affecting over 48,500 people every year. This disease is most common in those 75 and older. Also, being aware of risks like radon gas and pollution matters a lot. Knowing about lung cancer can help us prevent it and catch it early.
Want more info on lung cancer types? Check out detailed facts here. Understanding lung cancer’s details is key, including how it relates to other health issues.
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is divided into two main types: non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer. Each one has unique characteristics and different treatment options. They also differ in how common they are.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) accounts for about 80% of lung cancer cases. This makes it the most common form. NSCLC is divided into three main subtypes:
- Adenocarcinoma: This is the most common type of lung cancer in the U.S. It usually starts in the outer parts of the lungs.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type is often found closer to the middle of the lungs, next to the bronchi. It is strongly linked to smoking.
- Large Cell Carcinoma: This type grows and spreads quickly, making it very aggressive. Sometimes, it appears as a Pancoast tumor and is treated with chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) is found mostly in heavy smokers. Under a microscope, its cells look different from other cancer cells. This means it needs special treatment.
There are also rare lung tumors called lung carcinoid tumors. They grow slowly and are usually removed by surgery. Even though they are rare, some grow faster than others and can spread.
Causes and Risk Factors of Lung Cancer
The main cause of lung cancer is smoking. It is the biggest risk factor. About 90% of lung cancer cases are due to smoking. The more someone smokes, the higher their risk of getting lung cancer becomes.
Secondhand smoke is also dangerous. It is the third leading cause of lung cancer in the U.S. People who breathe in secondhand smoke have a higher chance of getting the disease. Radon gas is another major cause. It’s the second biggest cause among non-smokers, linked to about 30% of their lung cancer deaths. Shockingly, radon affects one in fifteen U.S. homes.
Working with asbestos can greatly increase lung cancer risk. Workers exposed to asbestos are much more likely to die from lung cancer. Also, if someone has had radiation therapy to the chest, they’re at a higher risk.
Genetics matter too. People with a family history of lung cancer have a higher risk. This risk increases further if many close relatives are affected.
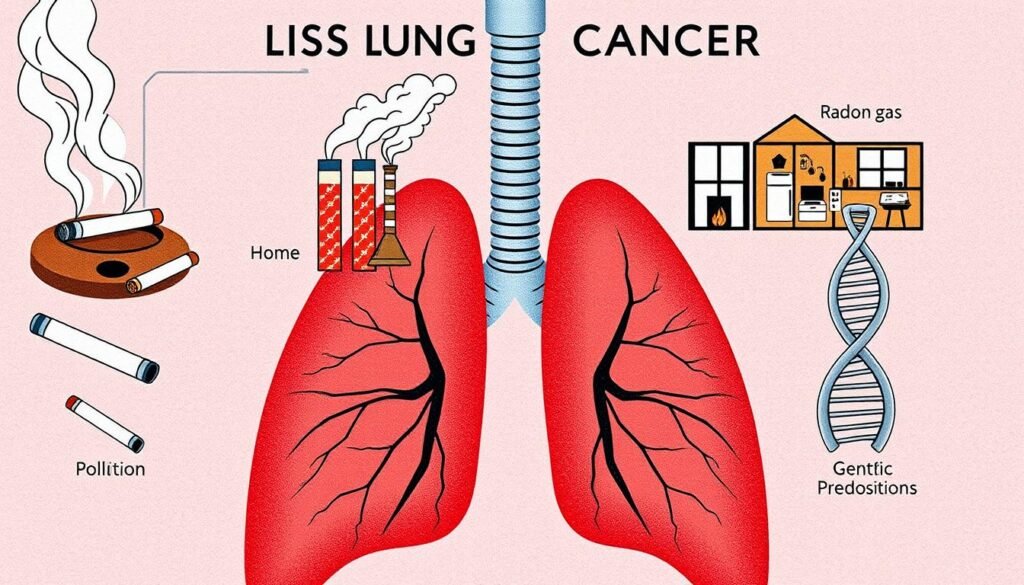
The effects of smoking marijuana and using e-cigarettes on lung cancer risk are still unclear. The FDA has warned about the risks of e-cigarettes, including lung damage. Air pollution plays a smaller role, causing 1% to 2% of lung cancer deaths. Knowing all the causes and risk factors is key for preventing lung cancer and catching it early.
Symptoms of Lung Cancer Both Lungs
Knowing the symptoms of lung cancer can help catch it early, which is key. Many people don’t see symptoms until it’s advanced. Spotting early symptoms can lead to quicker medical help and better chances for those affected.
Early Symptoms
Early lung cancer can look like common health issues. You might notice:
- A persistent cough lasting over eight weeks
- Fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest
- Unexplained weight loss or loss of appetite
- Recurring respiratory infections, like bronchitis or pneumonia
Even slight changes, like new wheezing, could be a warning. If you see these signs, get medical advice. For more on lung cancer signs, like swollen lymph nodes, visit this link.
Advanced Symptoms
When lung cancer gets worse, the symptoms are more severe. These include:
- Coughing up blood, even in small amounts
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breaths
- Shortness of breath caused by narrowed air passages
- Neurological symptoms like memory lapses or personality changes due to paraneoplastic syndromes
- Bone pain or swelling in lymph nodes as the cancer spreads to other areas
There can be other serious problems, like Horner syndrome or superior vena cava syndrome. Catching symptoms early can mean better treatment options and survival chances.
| Symptom | Stage |
|---|---|
| Persistent cough | Early |
| Coughing up blood | Advanced |
| Shortness of breath | Advanced |
| Chest pain | Advanced |
| Frequent infections | Early |
| Fatigue | Early |
Diagnosis and Staging of Lung Cancer
To diagnose lung cancer, doctors start with a detailed medical history and a physical exam. Imaging tests like chest X-rays and CT scans are vital. They look for unusual signs in the lungs. If something odd is found, more tests might be done.
A biopsy is usually next if lung cancer seems likely. It takes a bit of lung tissue to examine for cancer cells. After confirming cancer, it’s important to figure out the staging of lung cancer. This step helps decide the best treatment approach.
Non-small cell lung cancer stages go from 0 to IV. Stage 0 means cancer is only in the lung’s top lining. Stage I shows it hasn’t spread to lymph nodes or beyond. Stage IV is the most serious, with cancer spreading to other organs.
Small cell lung cancer is called limited or extensive. This is critical for figuring out treatment plans and outcomes.
Staging considers tumor size, lymph node involvement, and if cancer has spread. Getting the stage right is key for the right treatment plan. This can greatly affect patient prognosis.
The table below gives an overview of lung cancer staging and treatment:
| Stage | Description | Treatment Implications |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Affects top lining of the lung or bronchus | Often treated with surgery or targeted therapies |
| I | No spread to lymph nodes or other body parts | Surgery is commonly recommended |
| IV | Most advanced, may have spread to distant organs | Systemic therapies like chemotherapy or immunotherapy |
| Limited (Small Cell) | Cancer confined to one lung and nearby lymph nodes | Potential for localized treatment |
| Extensive (Small Cell) | Cancer has spread beyond the original location | Requires aggressive systemic treatment |
In conclusion, diagnosing and staging lung cancer involves a detailed process. Advanced imaging and biopsy are key steps. This careful approach is crucial for effective treatment plans, helping improve patient results.
Treatment Options for Lung Cancer
Lung cancer treatment varies by type, stage, and the patient’s health. The main kinds are non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Knowing the treatment options helps patients and families make informed care decisions.
Surgery
Surgery can work for non-small cell lung cancer if the cancer hasn’t spread. It aims to remove the tumor and nearby tissue. Early detection through screening improves the chance of successful surgery.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy, often paired with chemotherapy, is a choice for small cell lung cancer. It uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Stereotactic body radiotherapy, a more accurate type, may take only a few sessions, ideal for small cancers.
Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Chemotherapy, used alone or with radiation, aims to kill remaining cancer cells after surgery. Targeted therapy works against specific mutations in lung cancer. It’s especially useful for advanced or resistant cancers.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a breakthrough in lung cancer treatment. It boosts the immune system to fight cancer, used after surgery or as a main treatment. Research on new immunotherapy treatments is ongoing.
Some lung cancer patients try complementary medicines along with standard treatments. Palliative care, aimed at easing pain and improving life quality, is crucial. For risks tied to lung cancer, like the effect of smoking, see this link.
Managing Side Effects of Lung Cancer Treatment
Lung cancer treatment can lead to different side effects. These can greatly affect your life. Managing these side effects well is key to keep comfortable. Lung cancer treatment side effects like nausea, tiredness, and pain can be helped. This can be done through medicines and changing some lifestyle habits. Talking to your doctors and palliative care teams is important for complete symptom relief.
After chest radiotherapy, swallowing might get hard. Many people switch to a liquid diet because of this. Here are some tips to help with this problem:
- Eating softer foods like soup, porridge, mashed potatoes, yogurt, or custard.
- Not eating foods that are spicy, very hot, or cold to avoid irritation.
- Avoiding alcohol to reduce discomfort.
Nutritionists are key in advising on what to eat and suggesting foods that are high in calories to keep up nutrition. If you have pain or heartburn, doctors can prescribe medicines to help. Nausea is common too, and can make you vomit a lot. To feel better, you might:
- Try ginger and fizzy drinks.
- Use medicines to stop the sickness.
- Avoid fatty foods and big meals.
Using relaxation techniques like mindfulness can also help with symptoms. Breathing trouble is common during and after radiotherapy, affecting how well you can breathe. To deal with this, you can:
- Talk often with your medical team for quick evaluation.
- Get help from dietitians and healthcare pros for more support.
Many people feel out of breath for different reasons, like less lung function or fluid around the lungs. To handle fluid around the lungs, doctors might do certain procedures. Handling pain might need medicines, radiation therapy, and other methods. It’s crucial to take care of side effects like not eating much and losing weight. This helps keep you comfortable and keeps your quality of life high.
Using a team of experts to manage side effects focuses on care that puts patients first. It aims to improve life during this hard time.
| Side Effect | Management Strategies |
|---|---|
| Difficulty Swallowing | Soft foods, avoiding irritants, dietitian consultations |
| Nausea | Ginger, fizzy drinks, anti-sickness meds, mindful eating |
| Shortness of Breath | Regular medical check-ups, managing fluid accumulation |
| Pain | Medications, radiation, palliative approaches |
Living with Lung Cancer
Living with lung cancer comes with physical and emotional challenges. Patients must find a lifestyle that supports their well-being while dealing with their diagnosis. They need to use support systems, manage their condition well, and make lifestyle changes.
Making healthy choices is very important. Eating lots of fruits and vegetables and exercising can make you healthier during treatment. It’s very important to stop smoking, even if your lung cancer is advanced. This can help you live longer. Having a routine that includes these habits is key to coping and keeping symptoms in check.
Having a support network is crucial. Talking to doctors, joining support groups, and seeing counselors can help you deal with feelings and stress. Learning about lung cancer and treatments lets patients make better choices. Resources are available online to help with the emotional and practical parts of having lung cancer. They can improve your physical and mental health. For more info, please visit this link.
Here are some key points for living with lung cancer:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Physical Health | Focus on a balanced diet and regular exercise to enhance physical strength. |
| Mental Health | Engagement with professional counseling and support groups to handle emotional stress. |
| Symptom Management | Understanding symptoms like breathlessness and pain, and how to cope with them. |
| Financial Considerations | Exploring financial support options available to ease the economic burden. |
| Follow-Up Care | Regular follow-up visits are crucial for monitoring health and managing ongoing symptoms. |
Having a proactive attitude is key when living with lung cancer. It helps patients and their families face the future with courage and hope. Knowing about resources and building supportive relationships makes coping with lung cancer much easier.
Conclusion
Lung cancer leads to more deaths than any other cancer in the U.S. and worldwide. It highlights the need to understand its symptoms, types, and causes. In just 2010, around 239,320 new cases were reported in the U.S., with 161,250 deaths. This shows why raising awareness and education about this disease is crucial.
Treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy play key roles. But their success depends on the disease stage and the person’s unique situation. Early detection and specialized care are important. Yet, lung cancer’s 5-year survival rate stands at just 15.6%. This underlines the importance of research for better treatments.
The rise in lung cancer cases, mainly due to smoking, calls for strong public health efforts. Both healthcare professionals and government officials must work together to fight this disease. Practices like prevention and early detection are key. Together, we can aim to reduce lung cancer rates and give diagnosed individuals a better chance.