About 80% to 85% of lung cancers are Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Large Cell Carcinoma makes up 10% to 15% of these cases. It grows quickly and spreads fast, which makes finding and treating it early very important.
Knowing about Large Cell Carcinoma’s types, symptoms, and treatments is vital if you are diagnosed. While Small Cell Lung Cancer affects fewer people, NSCLC, including Large Cell Carcinoma, is a major concern. Remarkably, smoking causes nearly 90% of lung cancer cases. This shows how crucial it is to be aware and prevent it.
Treatment for lung cancer is getting better with options like chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Centers like Moffitt Cancer Center provide custom treatment plans. These plans meet the unique needs of those fighting this tough disease.
Key Takeaways
- Large Cell Carcinoma is a subtype of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, comprising 10-15% of cases.
- Smoking is responsible for nearly 90% of lung cancer cases.
- Rapid growth and spread characterize Large Cell Carcinoma, leading to serious symptoms.
- Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
- Staging utilizes the TNM system to categorize the extent of the disease.
- Early detection can significantly improve survival rates; combined 5-year survival for all stages of NSCLC is 24.9%.
Introduction to Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a major health issue in the United States, leading to many deaths every year. It is mainly categorized into Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). About 80% to 85% of cases are NSCLC.
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of NSCLC, followed by squamous cell carcinoma. Squamous cell carcinoma is often linked with smoking. Large cell carcinoma, known for its fast growth, is another type of NSCLC.
Small Cell Lung Cancer, making up 10% to 15% of cases, is especially aggressive. This type is closely tied to cigarette smoking. Knowing about lung cancer early can increase survival chances. It highlights the importance of being aware of the disease’s signs and risk factors.
What is Large Cell Carcinoma?
Large Cell Carcinoma is a type of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It’s known for its large cancer cells seen under a microscope. It groups various large cell cancers that can’t be otherwise classified. The lung carcinoma characteristics of this cancer make it very aggressive and quick to spread.
This cancer mainly affects the lungs and areas around them. Symptoms like coughing, breath shortness, and losing weight without trying can show up, signaling the cancer might be advancing. If not found early, treating this cancer becomes harder and survival chances may lower.
Understanding lung cancer is critical. Biomarker tests help find cancer’s genetic markers. This assists doctors in creating tailored treatment plans. Knowing the lung carcinoma characteristics is key for personalized treatments. This could lead to better results and fewer side effects.
| Stage | Description | Common Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Stage 0 | Localized cancer, no spread | Surgery, monitoring |
| Stage I | Localized tumor in the lung | Surgery, chemotherapy |
| Stage II | Tumor has spread to nearby lymph nodes | Radiation, chemotherapy, surgery |
| Stage III | More extensive lymph node involvement | Chemotherapy, radiation |
| Stage IV | Cancer has metastasized to other organs | Palliative care, targeted therapy |
It’s crucial to be aware of cancer stages. Catching cancer early can greatly improve treatment success and save lives. Recognizing the aggressive nature of Large Cell Carcinoma helps in fighting it more effectively.
Types of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Non-small cell lung cancer, or NSCLC, makes up about 80% of lung cancer cases. There are different kinds, each with its own traits and how they react to treatments. Main types include adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
Adenocarcinoma is usually found on the outer parts of the lung. It grows more slowly than other types, making it easier to treat. Squamous cell carcinoma, on the other hand, is closer to the middle of the lung, near the bronchus. It’s often related to smoking, which shows how lifestyle choices affect lung cancer risk.
Large cell carcinoma can be found anywhere in the lungs. It’s known for being aggressive, growing and spreading quickly. This means patients often need fast treatment.
There are also less common NSCLC subtypes. Carcinoid tumors grow slowly, and surgery usually works well. Pancoast tumors start at the lung’s top and might need chemo, radiation, and surgery.
| Subtype | Location | Growth Rate | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinoma | Outer lung | Slow | Surgery, Chemotherapy |
| Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Central lung (next to bronchus) | Moderate | Surgery, Radiation, Chemotherapy |
| Large Cell Carcinoma | Anywhere in the lung | Fast | Surgery, Chemotherapy |
| Carcinoid Tumor | Variable | Slow | Surgery |
| Pancoast Tumor | Apex of lung | Variable | Chemotherapy, Radiation, Surgery |
Symptoms of Large Cell Carcinoma
Knowing the signs of large cell carcinoma helps catch it early. Lung cancer shows different signs depending on the type and stage. Being aware of these can greatly improve treatment success.
Common Symptoms
Large cell carcinoma comes with several common signs. These include:
- Persistent cough
- Shortness of breath
- Coughing up blood
- Chest pain
Each symptom is key for spotting issues early. Early recognition leads to faster help, improving survival chances. When patients notice these signs, seeing a doctor is critical for a good check-up.
Symptoms of Advanced Stages
As the cancer grows, symptoms worsen and vary more. Signs of advanced cancer include:
- Jaundice
- Back pain
- Neurological issues like headaches or seizures
Metastasis, or spread of cancer, causes these severe signs. Anyone seeing these should get help right away. Catching it early can change the course of the disease and improve treatment approaches.
It’s crucial to understand all possible symptoms of large cell carcinoma. If symptoms get worse or you see new ones, contact a doctor quickly. This ensures you get the right care fast.
Causes and Risk Factors for Large Cell Carcinoma
It’s crucial to know the risk factors for lung cancer to help prevent it. Smoking is the main cause, responsible for 80% of lung cancer deaths. This includes direct smoking and secondhand smoke exposure, raising the risk of diseases like large cell carcinoma.
Environmental elements also play a role in lung cancer. Radon gas is the second top cause in the U.S, especially dangerous for non-smokers. Being exposed to asbestos increases the chance of lung cancer, even more for those who smoke. It can cause serious lung problems.
Outdoor air pollution, including diesel exhaust, causes about 1% to 2% of lung cancer deaths. Having radiation therapy in the chest can heighten the risk for smokers. Also, having a personal or family history of lung cancer significantly raises your risk.
Other risk factors might surprise you. For instance, smoking marijuana could increase lung cancer risk because of the harmful substances in the smoke. While e-cigarettes are being studied for their health effects, they are seen as tobacco products with possible risks. Yet, their direct link to lung cancer isn’t clear.
To prevent lung cancer, high-risk individuals should get regular screenings and try to live healthy. Quitting smoking is essential, and there are many resources to help with that. For more prevention tips and support, you can visit Mayo Clinic or learn about new treatments at Care Your Lungs.
| Risk Factors | Description |
|---|---|
| Smoking | Primary cause of lung cancer; associated with 80% of deaths |
| Radon | Second-leading cause; significant risk for non-smokers |
| Asbestos | Further increases risk, especially for smokers |
| Pollution | Contributes to 1-2% of lung cancer deaths in the U.S. |
| Radiation Therapy | Prior treatment can elevate risk for lung cancer |
| Family History | Increases personal risk significantly |
| Marijuana Smoking | Presence of tar and carcinogens may elevate risk |
| E-cigarettes | Potentially harmful, but direct cancer link uncertain |
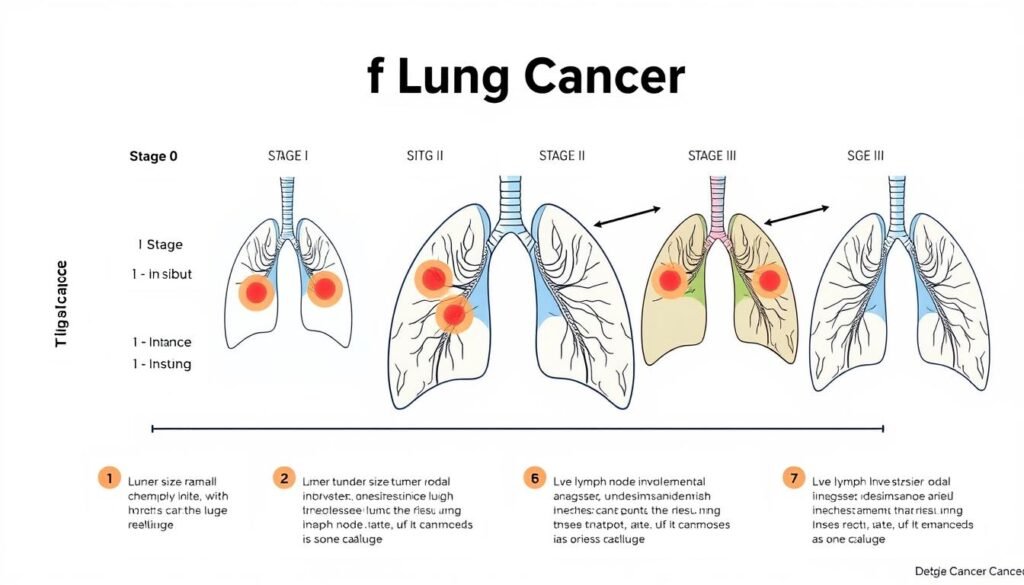
Lung Cancer Staging Explained
Lung cancer staging is crucial in treating this disease. It helps decide on the best treatment for patients. Staging uses the TNM system to understand how far cancer has spread. Knowing the stage helps choose treatments that are best for each patient.
The TNM Staging System
The TNM system classifies lung cancer using three factors: tumor size (T), lymph node involvement (N), and whether it has spread (M). This system outlines cancer stages from 0 to IV. Stage 0 is when cancer hasn’t spread, while stage IV is the most severe. The system helps decide the right treatment.
Understanding Staging with Large Cell Carcinoma
Large Cell Carcinoma also uses the TNM system for staging. It’s important for deciding how to treat it. Early stages mean cancer hasn’t spread much. Later stages show it has spread more and needs stronger treatment. This helps doctors plan the best care for their patients.
Diagnosis of Large Cell Carcinoma
Diagnosing Large Cell Carcinoma starts with a detailed medical history and physical check-up. Doctors look at symptoms and risk factors, like age and whether the person smokes. They then move on to Diagnostic Tests to find and stage the lung cancer.
X-rays and CT scans are key for seeing inside the lungs. These scans spot any unusual growths. After imaging, doing a Biopsy for Lung Cancer is crucial for confirming the diagnosis. Doctors may use different techniques to get tissue samples for this test.
Getting a quick and correct diagnosis of Large Cell Carcinoma is key to better treatment outcomes. The diagnostic process might include tests to find specific genes that help choose the best treatments. Knowing the exact type of lung cancer helps doctors plan the right treatment, which improves the chances of a good outcome. You can read more about the importance of diagnostics here.
Finding lung cancer early is crucial. It helps make treatment options more effective, which can greatly increase survival chances. The help of a specialized medical team is very important. They guide patients through diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer.
Treatment Options for Large Cell Carcinoma
Treatment options for Large Cell Carcinoma need a tailored approach. This is because the condition varies among patients. The plan may include different therapies based on the cancer stage, the patient’s health, and the tumor’s features.
Surgery
Surgery is key in treating Large Cell Carcinoma, mainly for those in early stages. Patients may undergo different surgeries such as:
- Lobectomy: This means taking out a lung lobe.
- Pneumonectomy: This is when one lung is completely removed.
- Wedge resection: This involves removing a small lung section.
These surgeries aim to remove as much cancer as possible. Doing this at the right time can lead to much better health outcomes.
Chemotherapy
After surgery, chemotherapy is often used to kill any remaining cancer cells. It can also be given before surgery to shrink the tumor. This makes it easier to remove. Studies show that timely chemotherapy can help patients with Large Cell Carcinoma live longer.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy can play a crucial role in treatment. It’s used when surgery isn’t an option or to get rid of any left-over cancer cells. Stereotactic body radiotherapy targets smaller tumors with precision. It keeps healthy tissue safe. Using radiation with chemotherapy can make treatment more effective.
Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy
Immunotherapy boosts the immune system to fight cancer. It works well for patients with certain PD-L1 levels. Targeted therapy attacks specific changes in cancer cells. It’s good for cancer that has spread or come back. Ongoing clinical trials are finding new ways to make these treatments even more personalized.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Large cell carcinoma prognosis is key for patient outcomes. Most patients, or 73.6%, are discovered at stages III or IV. At these stages, survival rates are lower. Stage I patients typically live for 42 months. However, those at stage IV live only about 3 months.
Survival rates for lung cancer are closely tied to treatment. For early stages, surgery can reduce death risk by 60%. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy can help stage IV patients too. Still, large cell carcinoma patients have a low five-year survival rate. It’s 11% for men and 14% for women.
According to the SEER database, many patients are over 70 when diagnosed. This makes treatment harder. Also, 98.4% of these cases are poorly differentiated, making treatment response tough.
Survival rates vary with the spread of the cancer. Localized cases have a better outlook, with a 65% five-year survival rate. But, those with widespread cancer face a 9% rate. Early detection and treatment greatly affect outcomes for this cancer type.
| Stage | Median Overall Survival | Five-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Stage I | 42 months | 65% |
| Stage II | 22 months | 37% |
| Stage III | 11 months | 9% |
| Stage IV | 3 months | 3% |
Knowing about large cell carcinoma and lung cancer survival helps us understand treatment success. Thankfully, new therapies are making things better for patients.
Support and Resources for Lung Cancer Patients
Patients with large cell carcinoma go through many challenges. Access to Lung Cancer Support can hugely improve their lives. Knowing about Patient Resources helps them deal with treatment and the disease’s impact.
The American Cancer Society and the National Cancer Institute play a big role in helping. They have programs like:
- CancerCare’s LUNGevity Helpline: Reachable at 844-360-LUNG (5864), it connects patients to experts for support and info.
- Financial Assistance: CancerCare gives financial help for cancer costs to eligible families, making treatment easier to afford.
- Coping Circle Workshops: These programs offer group support and address lung cancer concerns, sharing common experiences.
- Connect Education Workshops: Experts lead these, giving the latest info on cancer topics and empowering patients with knowledge.
Lung cancer-specific resources like booklets and fact sheets explain new treatments and how to handle side effects in a simple way. The Magnolia Meals at Home program delivers healthy meals to families dealing with cancer.
Sharing inspiring stories can lift the spirits of those touched by lung cancer. CancerCare shares hope and resilience stories, showing patients they’re not alone.

To sum up, connecting with Cancer Care Organizations helps medically and emotionally. It makes facing large cell carcinoma easier.
Understanding Large Cell Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Overview
Large Cell Carcinoma (LCC) is a type of lung cancer everyone should know about. It’s important to understand its symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options. This knowledge allows patients and families to make smart healthcare choices. The Summary of Large Cell Carcinoma shows LCC makes up about 3% of all lung cancers. It’s challenging to manage due to its rarity and complex nature.
Lung cancer statistics give us key insights into how common and deadly it is. For those with LCC, catching it early is crucial for a better chance of survival. Studies show that early diagnosis leads to more positive results than late treatment.
Biomarker testing is becoming key in creating personal treatment plans for lung cancer. Knowing the genetic factors helps tailor therapies for better results. Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma (LCNEC), a type of LCC, is rising in occurrence. It mostly impacts older men who have smoked heavily. Early symptom recognition and quick action are vital for better outcomes.
Resources like mentoring and financial help offer strong support during treatment. These resources help ease the stress and challenges of dealing with lung cancer. Having good support can lighten the emotional and logistical load of a diagnosis.
It’s crucial to understand large cell carcinoma to take charge of your health. Staying informed about lung cancer and being aware of symptoms and risks can lead to better health decisions. This proactive approach can significantly improve life quality.
Conclusion
It’s key to recognize the signs of Large Cell Carcinoma (LCLC) early. This lung cancer makes up 3%-9% of all cases. It’s especially risky for people who have smoked a lot. Being aware and careful about lung health can catch it early, helping treatment start sooner.
Those with LCLC face a tough journey, needing lots of different treatments. Options include surgery and chemotherapy. There are also newer treatments like targeted therapy and immunotherapy. These can help people live longer. The WHO has also shared updates on LCLC types, affecting how doctors treat it.
Keeping an eye on lung health is important. If you’re worried, see a doctor right away. Promoting Lung Cancer Awareness helps everyone learn more about this illness. This support is crucial for those dealing with their diagnosis and treatment. Together, we can fight large cell carcinoma better.