Cigarette smoking causes up to 90% of lung cancer deaths in the U.S. It’s a huge health issue. Understanding lung cancer risk factors and knowing the signs can save lives. This piece explains what causes lung cancer, including factors you can and can’t control.
Being aware of early signs like a lasting cough or losing weight without trying is key. Acting early improves chances of beating lung cancer. For more on early symptoms and risks, see this resource.
Key Takeaways
- About 80% to 90% of lung cancer deaths are linked to smoking.
- Smokers are 15 to 30 times more likely to develop lung cancer than non-smokers.
- Secondhand smoke is a significant risk factor for non-smokers.
- Radon exposure is the second-leading cause of lung cancer in the U.S.
- Asbestos and other occupational hazards significantly raise lung cancer risk.
- A family history of lung cancer can indicate increased personal risk.
Understanding Lung Cancer and Its Impact
Lung cancer is a major health issue, starting when abnormal cells in the lungs grow out of control. These cells may form tumors and harm nearby tissues. This disease comes in two main types: small cell and non-small cell lung cancer. Most people get it from smoking, the biggest cause. Lung cancer is the top reason for cancer deaths worldwide.
What is Lung Cancer?
To understand lung cancer, you must know how it forms and what makes it worse. It often begins with harmful substances like tobacco smoke changing cells. Other dangers include radon gas, workplace hazards, and past radiation therapy. Knowing these risks helps with early detection and preventing lung cancer.
Statistics on Lung Cancer Incidence
Lung cancer’s impact is clear in its high numbers and death rates. In the U.S., it causes about 25% of all cancer deaths. Each year, around 154,000 people die from lung cancer. This shows why we need more awareness and education on lung cancer risk factors.
| Year | Incidence Rate (per 100,000) | Mortality Rate (per 100,000) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 59.5 | 42.5 |
| 2021 | 58.9 | 41.7 |
| 2022 | 57.8 | 40.0 |
Understanding lung cancer deeply can lead to better health choices and reduce its impact. We must be active in fighting this tough disease.
Definition of a Risk Factor in Lung Cancer
Knowing what a risk factor in lung cancer is can help people manage their health. A risk factor is something that raises the chances of getting a disease. By understanding these, one can change their lifestyle or environment to lower lung cancer risks. Some risk factors, like smoking, can be changed. Others, like genetics, cannot.
What is a Risk Factor?
Lung cancer risk factors include traits or exposures increasing disease risk. Smoking is a key risk factor, causing about 85% of lung cancer cases. Being aware of risks from radon and asbestos is also critical. Learning about these can help people make healthier choices.
The Role of Risk Factors in Cancer Development
Risk factors play a huge role in cancer development. Exposure to them can change cells on a molecular level. This can lead to DNA mutations, abnormal cell growth, and eventually, tumors. Conditions like COPD and a family history of lung cancer increase risk too.
Also, working with dangerous chemicals can up lung cancer rates. Knowing these factors empowers people to make better health decisions.
Key Lung Cancer Causes
Lung cancer is a major health issue worldwide, with several factors leading to its occurrence. It’s crucial to know these causes to manage the risks linked to this disease. Smoking is the top cause of lung cancer. There are also other factors, like secondhand smoke and certain environmental conditions.
Smoking and Its Contribution to Lung Cancer
Smoking is the main reason behind lung cancer, causing most of its deaths. Smokers are 15 to 30 times more likely to get lung cancer than non-smokers. The risk increases with the amount and length of time smoked. This shows why stopping smoking is key for public health. Understanding how closely smoking is linked to lung cancer can push people to quit.
The Role of Secondhand Smoke Exposure
Secondhand smoke also leads to lung cancer in non-smokers. It’s dangerous for people who live or spend time with smokers. Studies show that secondhand smoke is a leading cause of lung cancer in the U.S. Knowing the risks can make smokers think about the impact on others.
Other Causes Beyond Smoking
Other things besides smoking can cause lung cancer too. Radon gas and asbestos are big risks, especially for smokers. Pollution also plays a part in increasing lung cancer risks. Learning about these other causes can help in prevention and shaping health policies.
| Cause | Percentage Contribution to Lung Cancer | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Smoking | 80-90% | Major risk factor with 15-30 times higher risk for smokers. |
| Secondhand Smoke Exposure | Varies | Third most common cause; significant risk for non-smokers. |
| Radon Gas | Small Percentage | Increased risk for smokers; leads to a limited number of cases. |
| Asbestos | Minor Contribution | Linked to lung cancer especially in occupational settings. |
| Air Pollution | 8% | Contribution to lung cancer cases in areas with high pollution. |
Lung Cancer Risk Factors You Can Change
It’s vital to know the lung cancer risk factors you can change. Certain lifestyle choices and environmental factors greatly affect your risk. By making informed changes, you can better your lung health.
Reducing Tobacco Use
One of the best ways to cut your lung cancer risk is to reduce tobacco use. Quitting smoking, even for those who have smoked for years, can greatly lower your chances. As time passes, your body starts to heal, lowering the risk even more.
Avoiding Secondhand Smoke
It’s equally crucial to avoid secondhand smoke for non-smokers. Being around someone else’s smoke can raise your lung cancer risk a lot. Keeping environments smoke-free helps protect you and your loved ones.
Mitigating Radon Gas Exposure
Dealing with radon gas exposure is another important step. Radon, a natural radioactive gas, can build up in homes, mainly basements. Testing for radon and taking steps to lower it can greatly cut lung cancer risk from this danger.

| Action | Impact on Lung Cancer Risk |
|---|---|
| Reduce tobacco use | Significant decrease in lung cancer risk |
| Avoid secondhand smoke | Protects against elevated lung cancer risks |
| Mitigate radon gas exposure | Reduces risk from a common environmental carcinogen |
Environmental and Occupational Exposures
Environment and work settings greatly affect lung cancer risks. Knowing these risks is key for prevention and awareness in different areas.
Asbestos Exposure Risks
Asbestos is a major environmental hazard linked to lung cancer. Workers in fields like construction, mining, and shipping face high risks. Breathing in asbestos fibers can seriously hike up lung cancer chances. Many studies show a strong tie between asbestos exposure and lung cancer deaths. This highlights the need for safety steps at work.
Impact of Air Pollution on Lung Cancer
Air pollution also leads to more lung cancer cases. Worldwide, outdoor air pollution causes about 108,000 lung cancer deaths each year. Also, using solid fuels for cooking and heating is linked to 36,000 deaths annually. These numbers show we must cut down air pollution to save lives.
Occupational Hazards and Carcinogens
Workplace hazards from cancer-causing agents are big risk factors for lung cancer. Carcinogens like diesel exhaust, arsenic, and vinyl chloride exist in many jobs, especially in smelting, metalworking, and making paper. In the US, 15% of lung cancer in men and 5% in women come from these job exposures. Fighting for better rules and safety practices is key to lowering these risks.
Lung Cancer Risk Factors You Cannot Change
Some lung cancer risk factors are beyond our control. These factors greatly affect someone’s chance of getting the disease. Key factors include genetics, age, and past radiation treatments.
Genetics and Family History
Our genes play a big role in lung cancer risks. If lung cancer runs in your family, your risk may double. This is due to genes passed down through families. Changes in genes such as CHEK2, BRCA1, and EGFR add to this risk. It’s crucial for people with a family history of lung cancer to know their risk.
Getting genetic counseling or testing can help people understand this risk.
Age as a Risk Factor
Age matters a lot when it comes to lung cancer. The older you get, the higher your risk. Lung cancer is most common in people over 65.
This fact highlights why regular check-ups are so important as we age. Staying aware and getting checked can lead to early discovery and treatment.
Previous Radiation Therapy
Having radiation therapy for other cancers can up your lung cancer risk. This risk gets even higher if you’ve smoked. It’s key for anyone treated for cancer before to keep an eye on their lung health.
For detailed info on lung cancer risks for nonsmokers, visit CDC’s lung cancer page. It covers stats and screening tips.
Emerging Research on Other Risk Factors
New studies are diving into less common factors that might increase the risk of lung cancer. They’re looking at the impacts of marijuana smoke and e-cigarettes, sparking new discussions. These sources, while not traditional tobacco, could pose significant health dangers.
The Effects of Marijuana Smoke
Marijuana smoke can be as harmful as tobacco smoke, with both containing cancer-causing agents. The link between marijuana and lung cancer is still being studied. While the results aren’t final, the risks are too important to ignore. Everyone should know these dangers when thinking about lung health.
E-cigarettes and Potential Risks
E-cigarettes have become popular as an alternative to smoking. But there are growing concerns about their safety. The FDA labels them as tobacco products, and they could harm the lungs. Studies are ongoing to find out more about e-cigarettes and lung cancer risks. It’s crucial to be aware of these dangers for your respiratory health.
Symptoms and Warning Signs of Lung Cancer
Knowing lung cancer symptoms early on helps with quick treatment. Often, people miss the first signs, which worsens health later. It’s key to know initial and advanced symptoms for fast help.
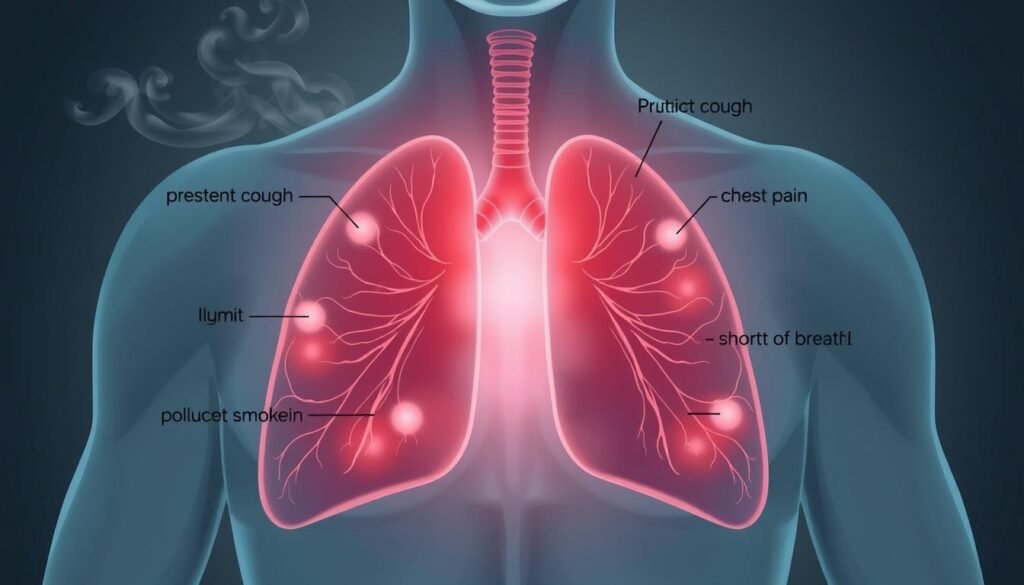
Early Warning Signs to Watch For
Early lung cancer signs can be quiet and mistaken for less serious issues. Look out for these signs:
- Persistent cough lasting longer than eight weeks
- Coughing up blood or bloody mucus
- Chest pain, especially with deep breaths or during coughing
- Hoarseness in voice
- Unexplained weight loss and loss of appetite
- Increased fatigue and shortness of breath
These signs might come from lung cancer syndromes. Conditions like Horner syndrome or Pancoast tumors can cause them.
Advanced Symptoms of Lung Cancer
When lung cancer gets worse, symptoms become more intense. Advanced stages may show:
- Bone pain
- Jaundice
- Lumps in the neck or collarbone area
- Repeated respiratory infections such as pneumonia
- Wheezing and recurring infections
At advanced stages, people might face paraneoplastic syndromes. These affect the endocrine and nervous systems, causing many problems. Quick checks of these symptoms by a doctor are key to getting the right treatment.
Prevention Strategies for Lung Cancer
To prevent lung cancer, combine healthy activities with proactive steps. This approach lowers risk significantly. It’s important to maintain a balance in your health routine and get screened often.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
To avoid lung cancer, making smart choices is key. The top choice is to quit smoking, which cuts risks a lot at any age. Avoiding harmful work environments and testing homes for radon also matters. Eating lots of fruits and veggies helps your health but doesn’t negate smoking’s dangers.
Regular Screening and Monitoring
Screening for lung cancer often is crucial for high-risk individuals. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force advises yearly screenings for 55 to 80-year-olds with a heavy smoking history. Early detection through these screenings increases chances for survival. You can find more screening info here.
Conclusion
It’s crucial to understand lung cancer risk factors for better prevention. This piece shed light on various risk elements. It shows how certain habits and genetics play a role in lung cancer, emphasizing the need for awareness.
Smoking is a top risk, making smokers highly likely to get lung cancer. Knowing this can help people choose healthier lifestyles. Also, spotting lung cancer signs early can save lives. Since lung cancer is often caught late, early detection is key. This means getting screened regularly, especially if you’re at high risk.
Every two minutes, someone in the U.S. is diagnosed with lung cancer. But, regular screening can cut death rates by up to 20%. This fact highlights just how important it is to get these checks done on time.
To wrap up, being informed about lung cancer risks can make a big difference. Understanding the role of environment, habits, and genes helps in prevention. Let’s all promote awareness and education to beat lung cancer’s high numbers.