Did you know about 1.6 million lung nodules are found by chance each year in the USA? Although ‘nodule’ sounds scary, 95% of these lung nodules are not cancerous. Having a spiculated lung nodule, known for its uneven edges, often makes people worry about cancer. But it’s important to know that not every spiculated lung nodule means cancer. In this article, we explore these nodules in detail. We correct common wrong ideas and share important lung cancer facts. This information aims to make lung health less confusing.
Key Takeaways
- Many spiculated lung nodules are not cancerous.
- Understanding lung nodules can alleviate anxiety.
- The majority of lung nodules require minimal intervention.
- Early detection significantly improves survival rates.
- Regular screenings are vital for early identification of potential malignancy.
- Consulting healthcare professionals is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Understanding Lung Nodules
Lung nodules are small, abnormal areas seen in the lungs. They often show up as white spots on CT scans or chest X-rays. Most adults find out they have them when getting checked for something else. Thankfully, less than 5% of these nodules are cancerous. Most are benign.
What Are Pulmonary Nodules?
Pulmonary nodules are small lung masses, usually under 3 cm wide. Knowing about them helps doctors check lung health. The features of pulmonary nodules include:
- Size: Less than 3 cm is considered normal.
- Shape: Nodules can be round or spiculated.
- Calcification: The presence or absence of calcification offers clues.
About 95% of nodules found in people 50 to 75, especially smokers, are not cancer. If a nodule doesn’t grow for two years, it’s probably not cancer.
Characteristics of Lung Nodules
The traits of lung nodules help tell if they might be cancer. It’s crucial to know the difference between harmless and harmful nodules. Important features are:
- Benign Nodules: Usually small, slow to grow, smooth, and round.
- Cancerous Nodules: Typically larger, quick to grow, bumpy, and can be semi-solid.
The details of a lung nodule can tell doctors about someone’s cancer risk. Factors include age, if they smoke, family cancer history, and exposure to things like asbestos. This info helps with diagnosis and treatment choices.
Types of Lung Nodules
There are two main types of lung nodules: benign and malignant. It’s vital to know the difference for proper diagnosis and treatment. Different causes lead to lung nodules. Recognizing these causes helps doctors figure out each nodule’s nature.
Benign vs. Malignant Nodules
Benign nodules are not cancerous and are more common than malignant ones. Hamartomas are the most common benign nodules, making up 55% of all benign lung tumors. These nodules make up about 8% of all lung tumors found. Studies show that 60% of nodules found in chest X-rays are benign. On the other hand, malignant tumors could be from lung cancer or cancer spreading from other parts of the body.
Common Causes of Nodules
Many different conditions can cause lung nodules. For benign nodules, common causes include:
- Granulomas: These often come from infections like tuberculosis or fungal infections.
- Hamartomas: These are benign tumors made from a mix of normal tissues.
Malignant tumors suggest serious health problems and are less common in people under 35. Finding out why nodules form is critical. Pulmonary nodules are quite common. They show up in about 1 in every 500 chest X-rays and 80% to 90% of all CT scans.
| Type of Nodule | Common Causes | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Benign Nodules | Granulomas, Hamartomas | 60% of nodules in chest X-rays |
| Malignant Tumors | Lung Cancer, Metastasis | Less common, 1% in those under 35 |
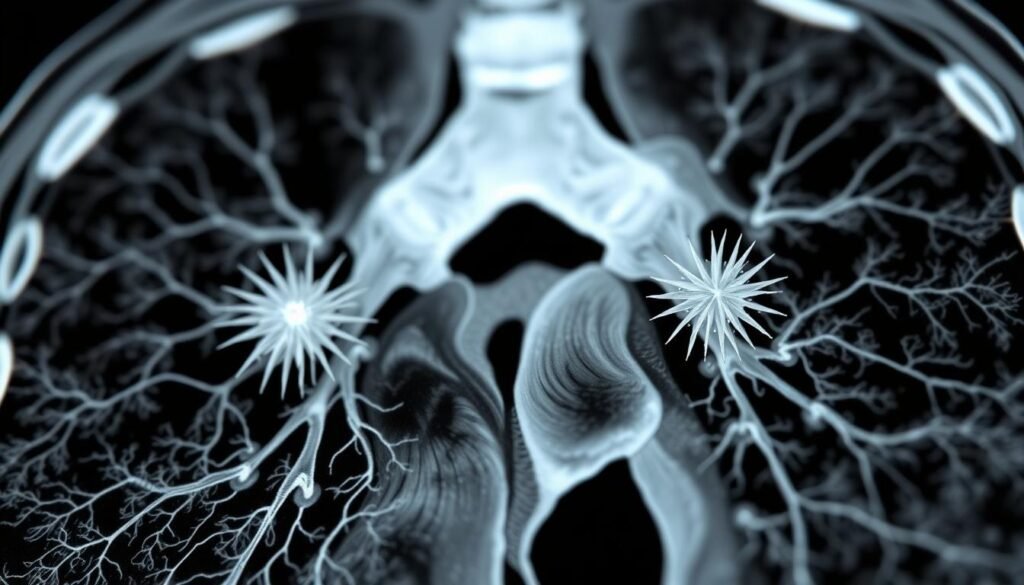
Is Spiculated Lung Nodule Always Cancer?
Spiculated nodules have traits that might signal cancer early on. They often have uneven edges. This ups the cancer risk. Most lung nodules are harmless, but about 40% of spiculated ones could be bad. For people over 50, the risk can jump to 50%.
Characteristics of Spiculated Nodules
Spiculated nodules are unique because of certain features. Here are key traits:
- Irregular borders, suggesting potential malignancy
- Rapid growth, with cancerous nodules doubling in size in about four months
- Larger size, as bigger nodules are more likely to be cancerous
Risk factors for these nodules include personal health history. Smokers over 50 are especially at risk. Knowing these features helps doctors diagnose and treat them. For example, a study used a special algorithm to spot spiculation better in lung scans. This tech makes diagnoses more accurate, helping patients get the right treatment .
Statistics on Malignancy
Lung cancer facts show worrying trends about spiculated nodules. Look at these important stats:
| Statistic | Percentage/Count |
|---|---|
| Probability of nodules being cancerous | ~40% |
| Nodules in smokers over 50 | ~50% malignant |
| Smokers vs. Never-smokers incidence of cancerous nodules | Higher in smokers |
| Presence of nodules in chest imaging (X-rays) | 1 in 500 |
| Presence of nodules in CT scans | 1 in 100 |
These stats stress the importance of careful checks on lung nodules. Nodules that are not standard, like spiculated ones, need more attention. Recognizing these signs is key. It leads to better treatment choices and helps patients get well.
The Role of CT Scans in Diagnosing Lung Nodules
CT scans play a key role in diagnosing lung nodules. They let doctors get clear images of the lungs. This makes it easier to check lung nodules well. CT scans can show the nodule’s size, shape, and edges better than X-rays can.
How CT Scans Work
During a CT scan, many X-ray images are taken from different angles. A computer puts these images together into detailed pictures. These pictures help doctors see nodules clearly. They can tell if a nodule is likely benign or malignant. Most lung nodules found by CT scans are not cancerous, especially if they are small and have smooth edges.
Limitations of CT Scans
CT scans are very useful, but they have limits. They can’t tell for sure if a nodule is cancer. If a nodule looks odd, like with irregular edges, doctors may get suspicious. But they will need to do more tests to know more, such as PET scans or biopsies.
A regular chest CT scan exposes you to more radiation than you’d get from nature in a year. It’s double, in fact. There’s a small risk of cancer from getting a CT scan. Doctors usually suggest follow-up CT scans that use much less radiation. These scans are safer.
Knowing the limits of CT scans helps us understand they’re part of a bigger process. It’s very important for people at high risk, like smokers or those with a family history of lung cancer. They need careful checks over time.
Importance of Biopsy for Accurate Diagnosis
A lung biopsy is vital when there’s a chance a lung nodule could be cancer. Knowing about the different biopsies helps decide the best method for each case.
Types of Biopsies
Biopsies vary depending on the nodule’s features and where it’s located. We have some common techniques:
- Needle Biopsy: A slim needle gets the sample. Imaging like CT scans guide it.
- Bronchoscopy: A tube goes through the airways to get tissue from the nodule.
- Surgical Biopsy: Sometimes, surgery is needed for hard-to-reach nodules.
When Is a Biopsy Recommended?
Deciding on a biopsy takes careful thought. CT scans are important for watching nodules, especially if they change. A biopsy is suggested if:
- The nodule grows or looks worrying on scans.
- Big nodules over 8mm seem likely to be cancer.
- Nodules stick around or new symptoms suggest a closer look is needed.
A pathologist looks at the biopsy to check for cancer, infections, or other issues. The results guide what comes next, like more check-ups, seeing experts, or starting treatments based on the diagnosis.
Risk Factors for Lung Cancer
It’s crucial to know what increases lung cancer risk. Many things play a part in this. Age, gender, and smoking significantly affect lung cancer risks.
Age and Gender Considerations
Getting older raises the chance of having lung cancer. Most people diagnosed are over 50. But, younger folks, especially under 35, are less likely to get it. Men are more prone to lung cancer than women.
Impact of Smoking
Smoking is a big factor for lung cancer. It causes about 90% of lung cancer deaths in the U.S., says the CDC. Smokers, even those who’ve quit, face a high risk. Second-hand smoke and radon also increase your chances.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Higher risk in individuals over 50 years old |
| Gender | Men are more likely to develop lung cancer than women |
| Smoking | Responsible for up to 90% of lung cancer deaths |
| Second-hand Smoke | Increases lung cancer risk in non-smokers |
| Radon Exposure | Long-term exposure heightens the risk of lung cancer |
Lung Nodule Characteristics That Indicate Malignancy
It’s vital to know about lung nodules when thinking about cancer risk. Size and how fast they grow are key clues. Big nodules or ones that grow quickly are red flags and need more checking.
Size and Shape of Nodules
The size and shape of lung nodules can hint at cancer. Nodules over 3 cm are often more worrisome. Odd shapes are especially concerning. Studies show that nodules 8 mm and up are likely to be cancerous. Yet, tiny nodules under 5 mm are usually harmless, more so in certain lung areas.
Growth Rate Analysis
How fast a nodule grows tells us a lot. Malignant nodules might double in less than four months; some even quicker, in 25 days. This fast growth is unlike benign nodules, which hardly grow. Knowing this growth speed helps doctors tell apart cancerous from safe nodules.
| Characteristic | Malignant Nodules | Benign Nodules |
|---|---|---|
| Size | More than 3 cm & 8 mm or larger | Less than 5 mm |
| Growth Rate | Doubles every 4 months (or faster) | Very little growth or change |
| Shape | Irregular | Typically round |
| Distribution | Non-calcified, ground-glass appearance | Commonly in fissures, with calcification |
If you’re worried about lung health, know these signs. Talking to your doctor early can make a big difference. Early checks and stopping smoking are key to fight lung cancer. For more info, especially on smoking’s role, read this detailed article.
The Benefits of Early Detection of Lung Cancer
Finding lung cancer early can greatly improve survival rates. If caught early, treatment is much more successful. It’s vital to have regular check-ups and know the symptoms, especially for those at greater risk.
Survival Rates
Early detection significantly boosts the chances of surviving lung cancer. The stage of cancer at diagnosis affects survival rates:
| Stage | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|
| Localized | 60-80% |
| Regional | 30-50% |
| Metastatic | Less than 5% |
This data shows how crucial early action is. For cancers caught when still localized, outcomes and chances of beating it are much better.
Effectiveness of Treatment Options
Treatments work best when lung cancer is found early. Options like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation are more successful then. If the cancer hasn’t spread, surgeries like lobectomy can be highly successful. Also, technologies like CT scans and PET/CT help spot cancer early, which is key for effective treatment.
There’s a growing push for early lung cancer detection. Better screening leads to better chances of beating cancer. This effort is changing lives for many facing lung cancer.
What to Do If You Have a Spiculated Lung Nodule
Finding out you have a spiculated lung nodule can be scary. You might feel a lot of things and have many questions. It’s important to act fast and smart after finding out. The first step is to see a pulmonologist. This doctor knows a lot about lungs and breathing problems. They can explain what’s going on and what tests you might need.
Consulting a Specialist
Meeting with a pulmonologist is important. They know how to check the nodule by looking at its size and other features. They’ll suggest important tests to figure out what it is. This could include special scans or even a biopsy to see if it’s cancer. Choosing a doctor you trust can make a big difference. It helps you understand more and make good choices.
Understanding Your Testing Options
Knowing what tests you can take is key. Different tests help understand what the nodule is:
- Low-Dose CT Scans: Good for telling apart harmless from harmful nodules.
- Biopsy: Taking a piece of the nodule to examine it closely.
- Follow-Up Imaging: Checking the nodule over time for any changes.
It’s smart to know the good and bad sides of each test. This knowledge helps patients decide what’s best for them.
| Testing Options | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| CT Scans | A non-invasive imaging technique. | Used for initial assessment and follow-up. |
| Biopsy | A procedure where a sample of lung tissue is taken. | To confirm diagnosis through pathological analysis. |
| Chest X-Rays | Another imaging option, though less detailed. | Initial screening and monitoring over time. |
With good advice and knowing the tests, patients can face this tough time with confidence. It’s crucial to see a doctor quickly and follow a clear plan for the best care.
Available Treatments for Malignant Lung Nodules
Managing malignant lung nodules effectively requires a special plan. This plan looks at the cancer’s unique features and the patient’s health. There are mainly two types of treatments: surgery and non-surgery.
Surgical Options
Surgery is key for treating malignant lung nodules. The top surgeries are:
- Lobectomy: This removes an entire lung lobe and works well for big nodules.
- Wedge resection: It takes out a small piece of lung with the nodule. It’s not as big of a surgery.
Clinical trials show that some surgeries can lead to a 5-year survival rate of about 80%. This is great news for those with early-stage cancers. The choice between lobectomy and wedge resection depends on the nodule’s size, its place, and what the patient wants.
Non-Surgical Treatment Avenues
If surgery isn’t an option, there are other ways to treat the nodules. These include:
- Chemotherapy: This kills cancer cells. It’s often used with surgery.
- Radiation therapy: This targets the nodules to control growth and ease symptoms.
Making a choice between surgery and non-surgery involves thorough checks. For more on how to manage these nodules, visit here.
| Treatment Type | Purpose | Common Procedures |
|---|---|---|
| Surgical | Remove cancerous tissue | Lobectomy, Wedge resection |
| Non-Surgical | Manage symptoms, prevent growth | Chemotherapy, Radiation therapy |
Current Research and Clinical Trials
The field of lung cancer treatment is always changing thanks to new research. Advances in clinical trials aim to find better ways to help patients. These trials test new methods and treatments.
Innovations in Lung Cancer Treatment
There are exciting developments in treatment as researchers look into different methods including:
- Targeted therapies: These treatments attack only cancer cells, saving healthy cells. This reduces side effects.
- Immunotherapy: It boosts the body’s own defenses to fight cancer.
- Advanced imaging techniques: These methods make diagnosing more accurate, which helps in planning treatment.
Participating in Clinical Trials
For those with lung nodules, being in a clinical trial is an opportunity. These trials offer new treatments that are not yet common. Patients get to try the latest in lung cancer care. Being part of a trial also helps research. It adds to the knowledge that can help others in the future.
Conclusion
The task of diagnosing spiculated lung nodules shows how vital it is to be aware of lung cancer. It also shows why detailed diagnostic procedures are needed. Lung cancer is the top reason people die from cancer in many countries. It’s key to know the risks and features of these nodules. For instance, nodules over 10 mm are more likely to be cancerous. Finding them early is crucial for helping patients.
Research shows small nodules are often not cancerous. But, as they get bigger and show certain features on scans, the cancer risk goes up. Many times, imaging tests don’t catch these nodules. This makes it important for people to see specialists. These experts use CT scans, biopsies, and careful monitoring. This helps patients understand their risk and what tests they might need.
Knowing more about spiculated lung nodules can save lives. When we catch these nodules early and watch for lung cancer signs, we can do a lot. This helps patients and doctors act fast for the best health results.