Small cell lung cancer makes up about 15% of all lung cancer cases. It grows quickly and spreads fast. This cancer is mainly linked to smoking. It causes big problems for patients and doctors. Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) is when the cancer has spread a lot. It can affect both lungs or other parts of the body. This guide talks about treatments for lung cancer, new therapies, care to make patients more comfortable, and what patients can expect.
We wrote this article to help patients and their families understand Extensive Stage SCLC. Our goal is to help them make good decisions to improve their lives.
Key Takeaways
- Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer accounts for a significant portion of lung cancer cases.
- Early detection and treatment options such as chemotherapy can greatly impact survival rates.
- Understanding symptoms is critical for timely diagnosis and intervention.
- Palliative care plays a vital role in managing symptoms and enhancing quality of life.
- Engaging in clinical trials may provide access to emerging treatments for SCLC.
Understanding Small Cell Lung Cancer
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive type of lung cancer, mainly seen in smokers. It makes up about 14% of lung cancers in the U.S., affecting roughly 31,000 people each year. Because it spreads fast, finding and treating SCLC early is challenging.
What is Small Cell Lung Cancer?
This cancer starts in the lungs’ neuroendocrine cells and is more aggressive than non-small cell lung cancer. People with SCLC often have a constant cough, feel short of breath, and lose weight without trying. Detecting and treating it early is crucial because of how quickly it grows. Doctors use imaging tests, biopsies, and staging to see how far the cancer has spread.
How Does Small Cell Lung Cancer Develop?
Smoking and being around certain chemicals can lead to Small Cell Lung Cancer. When SCLC spreads, it’s called extensive stage disease. It’s important to notice symptoms early and understand how the cancer grows. For more information on treating this cancer, including chemotherapy and immunotherapy, this guide to Small Cell Lung Cancer is helpful.
Stages of Small Cell Lung Cancer
It’s crucial to know the stages of small cell lung cancer for treatment and prognosis. There are two main stages: Limited Stage and Extensive Stage. Knowing the stage helps decide how to manage and treat the cancer.
Limited Stage vs. Extensive Stage
In Limited Stage, cancer is only in one lung and possibly nearby lymph nodes. This allows doctors to use aggressive treatments like surgery. These treatments can help people live longer. But, in Extensive Stage, cancer has spread more widely. It may reach the other lung or distant organs. Then, a mix of treatments is used to control the spread.
Overview of the TNM Staging System
The TNM system is used to detail lung cancer stages. It checks Tumor size, Node involvement, and Metastasis. This system helps doctors decide the best treatment. To learn more about TNM and lung cancer, check out Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center.
| Stage | Definition | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Stage | Cancer confined to one lung or nearby lymph nodes | Surgery, chemotherapy |
| Extensive Stage | Cancer spread to both lungs or distant organs | Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy |
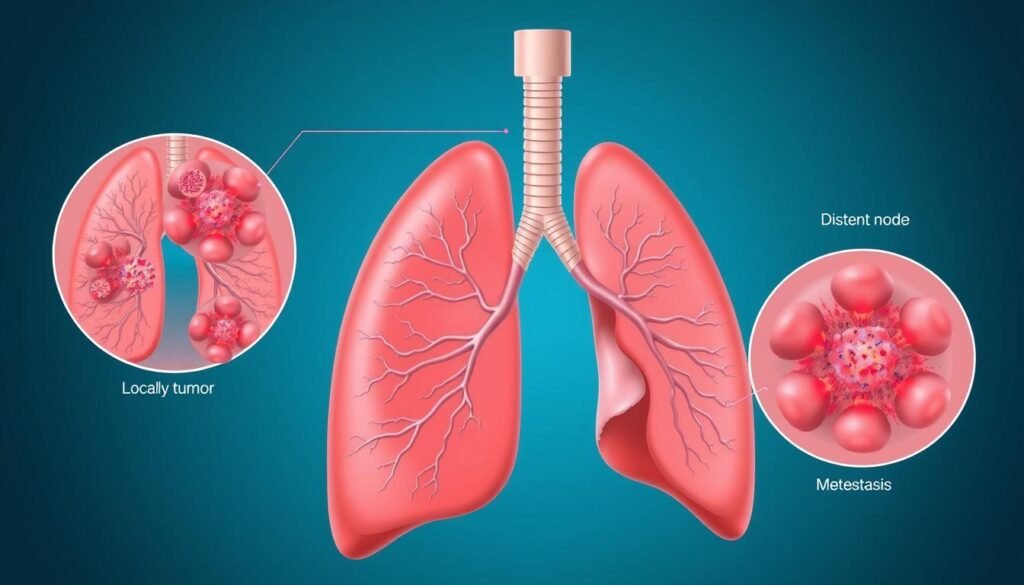
Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (ES-SCLC) is a serious type of lung cancer. It spreads far beyond the lungs, even reaching other organs or fluid spaces. Early detection is crucial because it greatly affects both the prognosis and the treatment options available.
Defining Extensive Stage SCLC
ES-SCLC is a late stage of cancer that about 70-80% of patients have when first diagnosed. The cancer may cover both lungs, touch the lymph nodes around them, or spread to other parts of the body. Key gene changes, like TP53 and Rb1 inactivation, often play a role. Since this cancer moves fast, knowing its traits is key to managing it well.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Extensive Stage
People with Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer face many hard symptoms. These can really reduce someone’s quality of life. Key symptoms are:
- Persistent cough
- Chest pain
- Significant weight loss
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
Spotting these symptoms early is important. It can lead to quicker action, which may improve how well treatments work. Yet, ES-SCLC’s future outcomes are often not very good, with a high chance of the cancer coming back. This fact highlights why it’s vital to keep track of symptoms and look into joining clinical studies for new treatments.

| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Prevalence of ES-SCLC | Affects 70-80% of patients at initial diagnosis |
| Common Symptoms | Persistent cough, chest pain, weight loss, fatigue |
| Genetic Alterations | TP53, Rb1 inactivation, SOX2 amplification, MYC family alterations |
| Treatment Challenges | High recurrence rates; advanced and often non-surgical |
Treatment Options for Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
Dealing with extensive stage small cell lung cancer involves several strategies. The main focus is on controlling the disease and making life better for the patient. Many need intense treatments because of how serious the disease is.
Chemotherapy as a Primary Treatment
Chemotherapy is key in treating this type of lung cancer. It often uses drugs like carboplatin and etoposide. Patients usually get chemotherapy every three weeks. This gives them time to recover between treatments.
The success rate for this treatment is about 70%. That’s impressive, considering how fast this cancer grows. But, side effects like tiredness, losing hair, and feeling sick are big hurdles.
Immunotherapy and its Role
Immunotherapy is now a crucial part of the treatment plan. It’s used alongside chemotherapy. Drugs such as atezolizumab and durvalumab are common choices. They boost the immune system’s fight against cancer.
More research shows how important immunotherapy is for this cancer.
Radiation Therapy for Symptomatic Relief
Radiation therapy helps with symptoms like pain or trouble breathing. While it’s a go-to during early stages of the disease, its use in extensive stages depends on what the patient needs. Patients might have treatments twice a day for three weeks or once a day for six weeks.
Side effects, like feeling tired and skin turning red, can happen. But, they are usually under control.
Knowing all the treatment options for extensive stage small cell lung cancer helps both patients and doctors. They can work together better to tackle the disease. For more details on these treatments, check out this guide.
| Treatment Type | Description | Common Drugs | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemotherapy | Primary treatment approach targeting rapid cell growth. | Carboplatin, Etoposide | Fatigue, Hair loss, Nausea |
| Immunotherapy | Enhances the body’s immune response to fight cancer. | Atezolizumab, Durvalumab | Possible immune-related side effects |
| Radiation Therapy | Alleviates symptoms such as pain and difficulty breathing. | Local radiation treatments | Fatigue, Skin reddening |
Clinical Trials and Experimental Treatments
Clinical trials are key in developing treatments for Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). They test new drugs and combinations of treatments. This offers newer options that might improve patient outcomes. Being part of a clinical trial can give access to experimental treatments not available in standard care.
Importance of Clinical Trials in SCLC Treatment
Clinical trials are vital for finding effective therapies against SCLC. They test new therapies that target the disease better. These tests check how well the treatments work and their safety. They give important info about how these new treatments compare to current ones.
Emerging Therapies and Future Trends
Targeted treatments and immunotherapies are exciting new therapies. For example, tarlatamab has led to significant tumor shrinkage in many patients. About 40% of people in these trials saw a positive response, which is much better than with older therapies.
The approach to treating SCLC is changing with a move towards personalized medicine. This means clinical trials are more important than ever. They offer hope for better survival rates. And they’re bringing in a new era of treatments made just for the needs of patients with extensive Stage SCLC.
Palliative Care in Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer
Palliative care is vital for patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer (SCLC). It aims to improve life quality by easing symptoms and offering support. It covers physical, emotional, and social needs for complete care during the patient’s journey.
The Role of Palliative Care
The main aim of palliative care in extensive stage SCLC is comfort and symptom management. Teams of doctors, nurses, social workers, and counselors come together. They create personalized care plans focusing on managing symptoms. These plans include:
- Pain relief strategies
- Support for emotional distress
- Assistance with daily living activities
Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Patients often experience breathlessness due to fluid or tumors blocking airways. Various procedures help manage these issues:
| Procedure | Description | Use (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Thoracentesis | Extraction of fluid from around the lung. | X% |
| Pleurodesis | Prevents fluid accumulation using substances such as talc or chemotherapy. | X% |
| Pericardiocentesis | Drains fluid around the heart. | X% |
| PDT (Photodynamic Therapy) | Opens blocked airways to improve breathing. | X% |
| Stent Placement | Inserts a stent to maintain airway patency. | X% |
Using these methods, healthcare workers greatly enhance a patient’s life quality. Timely symptom management helps patients face tough times with dignity and comfort. This shows why palliative care is crucial in treating extensive stage small cell lung cancer.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
It’s vital for patients and their families to understand the outlook and survival for Extensive Stage SCLC. About 65% of new small cell lung cancer cases are in the extensive stage. This shows how serious the disease can get. Without treatment, people with this condition live only 2 to 4 months after finding out they have it. This fact underlines the need for quick detection and action.
Understanding Survival Statistics for SCLC
Treatment can extend survival for extensive SCLC to 7 to 11 months. Chemotherapy is key, but adding drugs like Tecentriq (atezolizumab) and Imfinzi (durvalumab) can help too. With treatment, the 5-year survival rate for this cancer is still under 2%. Also, the cancer often comes back – over 80% do within the first year after treatment.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
Many things affect the outlook for those with extensive SCLC. A patient’s general health, how they react to treatment, and the cancer’s specifics matter a lot. Survival rates differ widely. For example, local SCLC has a 30% 5-year survival rate. But distant SCLC falls dramatically to 3%. Knowing these differences helps patients understand what they’re facing. To get detailed survival rate information, check out this survival guide.
Managing Side Effects of Treatment
Patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer often face many side effects. These effects come from chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Understanding and managing these side effects is key to improving life during treatment.
Common Side Effects of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a main treatment for this lung cancer. But, it leads to tough side effects. A major one is a drop in blood counts caused by its effect on the bone marrow. This drop can make patients feel more tired, get infections easily, and lead to anemia. Other common side effects are:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair loss
- Loss of appetite
- Mouth sores
Knowing about these side effects helps patients and caregivers get ready. It lets them seek help when it’s needed for a better treatment journey.
Addressing the Impact of Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is used with chemotherapy to fight cancer cells. It uses high-energy x-rays on the cancer. Even though it helps, it also has side effects that need managing. Common side effects from radiation therapy are:
- Fatigue
- Skin irritation or redness
- Difficult or painful swallowing
Knowing about these side effects lets patients tell their doctors early. This way, they can get help quickly. Support can reduce discomfort and make treatment better.
Conclusion
Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) comes with challenges. It highlights the need for a varied treatment plan. A vast majority of SCLC patients, around 80-85%, are diagnosed at this advanced stage. Knowing what treatments are out there helps improve care for these patients.
Recent steps forward, especially combining chemo with immunotherapy and antiangiogenic therapies, have changed the game. This shift offers new hopes for patients fighting this tough cancer.
There’s evidence that even with extensive-stage SCLC, some patients see long-term survival. Through various treatments, some have lived up to 50 months. This shows the power of mixing different therapies and underlines the importance of research. This research helps find better ways to fight the cancer.
New strategies, like immunotherapy, offer promise. They aim to lengthen the time patients live without cancer getting worse. This brings a glimmer of hope for better SCLC management.
Working together, healthcare teams and clinical trials push treatment forward for Extensive Stage SCLC. With new therapies emerging, patients have better chances for a longer, healthier life. For deeper understanding, check out this study.