It’s shocking, but 10% to 20% of lung cancers are in people who’ve never smoked much, if at all. This means there are 20,000 to 40,000 such cases yearly in the U.S. alone. Lung cancer in non-smokers is not just uncommon. It’s a big health issue that needs more attention.
Many don’t know that secondhand smoke exposure, radon gas, and genetics can cause lung cancer in non-smokers. Thinking it’s only a smoker’s disease can delay finding it early. This makes treatment harder. Knowing what causes it and its symptoms can help. For more, check lung cancer early signs and symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Approximately 10–15 percent of lung cancer patients in North America are non-smokers.
- Over 7,300 lung cancer deaths annually in the U.S. are linked to secondhand smoke exposure.
- Common risk factors for non-smokers include radon, asbestos, and pollution.
- Lung cancer can also have a genetic component, with about 8 percent being inherited.
- Recognizing symptoms early can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
Understanding Lung Cancer in Non-Smokers
Lung cancer isn’t just a smoker’s issue. It’s also a risk for people who’ve never smoked. Factors like genetic predispositions and environmental exposures play a role. This shows we need a broader view on what causes lung cancer.
About 19 percent of women in the U.S. with lung cancer never smoked. This is compared to 9 percent of men. Non-smokers mainly get a type called adenocarcinoma. On average, they are 67 when diagnosed, hinting at late detection.
The causes of lung cancer in non-smokers can be quite different from smokers. There are specific mutations, such as EGFR and ALK, seen more in non-smokers. It’s crucial to see lung cancer as a complex disease. It’s not just linked to smoking but has many other factors.
Statistics on Lung Cancer Among Non-Smokers
Lung cancer stats show more non-smokers getting sick. In the US, those never smoked but got lung cancer rose from 8 percent in 1990-1995 to 15 percent in 2011-2013. This shift makes us more aware of the lung cancer risk for non-smokers.
Now, adenocarcinoma is the top lung cancer in non-smokers. Each year, 20,000 to 40,000 lung cancers happen in non-smokers. The CDC says secondhand smoke causes about 7,000 of these. Another 3,000 are due to radon exposure.
Non-smokers’ lung cancers often have mutations making treatment easier. These mutations show up in 75 percent of non-smoker cases. But only 15-20 percent of smokers’ cancers have them. Adenocarcinoma is a major problem, making up over 30 percent of all lung cancers. It mostly hits women and the young.
In the UK, lung cancer in never-smokers doubled from 2008 to 2014. It went from 13 percent to 28 percent. As most lung cancers in non-smokers are not due to smoking, we need more awareness. There’s a big need for research on what causes lung cancer in non-smokers.
Common Misconceptions About Lung Cancer
Lung cancer myths often cause people to misunderstand who is at risk. Many think only smokers can get lung cancer. However, 10-20% of lung cancer cases occur in those who’ve never smoked. This shows how important it is to correct the false beliefs about lung cancer. Many believe they’re not at risk if they don’t smoke.
Some think lung cancer only affects older adults. But about 1% of cases are in young people. Research is being done on almost 100 young patients. The goal is to find out why some under 40 get lung cancer.
Many myths also exist about risk factors and genes. Some families have a higher risk because of the eGFR gene mutation. Yet, only 5 to 10 percent of cancers come from harmful inherited mutations. This means other factors also play a big role in cancer risk.
The stigma around lung cancer can stop people from getting help. Guilt over smoking can keep them from seeking treatments or trials. That’s why it’s key to teach the truth about lung cancer myths. Knowing the truth helps those affected by the disease. For more info, check out misconceptions about lung cancer.
| Myth | Fact |
|---|---|
| Only smokers can develop lung cancer | 10-20% of lung cancer patients have never smoked |
| Lung cancer only affects older adults | Young patients ( |
| Inherited mutations are the main cause of lung cancer | 5-10% of cancers are linked to inherited mutations |
| Lung cancer is a guaranteed death sentence | 5-year survival rate for all cancers is about 69% |
Risk Factors for Lung Cancer Not Caused by Smoking
Learning about non-smoking lung cancer risks is essential. It helps in prevention and raising awareness. Knowing these risks can lower the disease rate in non-smokers.
Secondhand Smoke Exposure
Secondhand smoke is very harmful. It causes around 7,300 lung cancer deaths yearly in non-smokers. Smoke from others’ cigarettes endangers everyone, especially kids and pregnant women.
It’s crucial to have smoke-free places to reduce these dangers.
Radon Exposure
Radon is a top concern, right after smoking. It’s a radioactive gas from natural uranium decay. It’s found in soil and rock and can build up inside houses.
Each year, radon causes about 2,900 lung cancer cases in people who don’t smoke. Testing homes for radon regularly is very important.
Asbestos Exposure
Being around asbestos is highly risky. This is true for those in construction or shipbuilding. When asbestos fibers get into the air and are breathed in, they are dangerous.
This exposure can lead to lung cancer and other serious lung diseases.
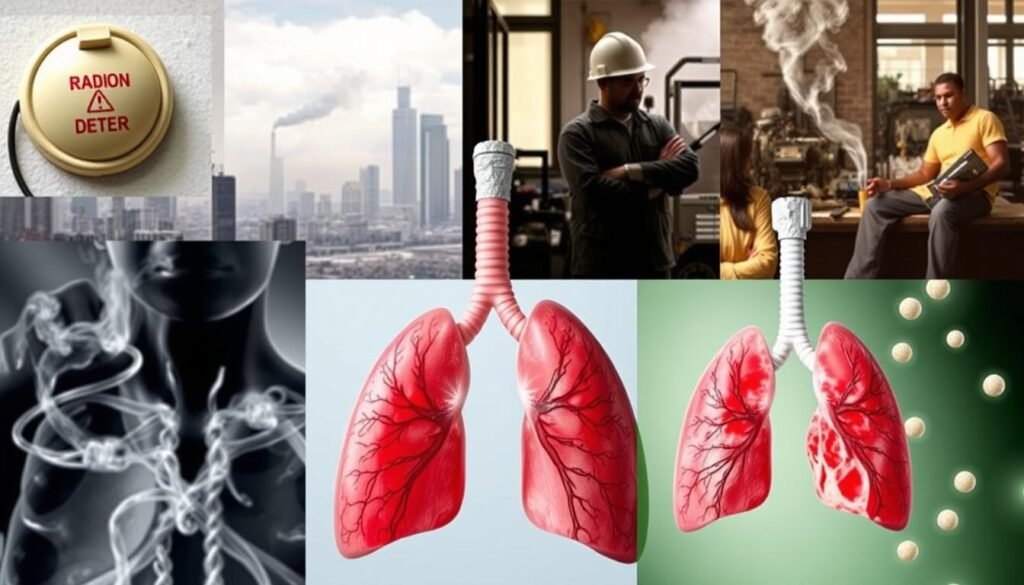

Environmental Factors Contributing to Lung Cancer
It’s key to understand how the environment affects lung cancer in non-smokers. Things like air pollution and exposure to dangerous substances play a big role. Knowing about these can help us make better choices to prevent it.
Air Pollution and Lung Cancer Risks
Air pollution is a major factor in lung cancer, especially in cities with lots of cars. Studies show that bad air particles increase the risk of getting lung cancer. This includes smoke from trucks, power plants, and burning wood, which is harmful to everyone.
Occupational Exposures to Carcinogens
Some jobs can make people more likely to get lung cancer. This happens in jobs where workers are around harmful materials like arsenic, asbestos, and uranium. Other substances like cadmium and chromium are also dangerous. This shows how important it is to have safety measures at work to reduce risks.
Genetic Factors in Lung Cancer Development
Understanding genetic factors is crucial in lung cancer studies, especially in non-smokers. Research shows that certain DNA mutations play a big role. These genetic changes and how they affect lung cancer are gaining attention.
The Role of DNA Mutations
DNA mutations are key in lung cancer development. For instance, mutations in the EGFR gene are common in non-smokers with lung cancer. These mutations guide treatment choices. Targeted therapies for these genetic changes can boost patient outcomes. Testing for mutations can allow for customized treatment plans and shed light on hereditary risks.
Hereditary Risks and Family History
If lung cancer runs in a family, there may be higher hereditary risks. Genetic factors greatly influence lung cancer risk. It’s vital for those with family history to talk to their healthcare providers. Early steps and preventive measures can be invaluable. They help people understand their risk and may lead to early screenings or lifestyle adjustments. For more info, check out resources about lung cancer risk factors here.

| Type of Genetic Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| DNA Mutations | Alterations in genes, particularly EGFR, linked to lung cancer. |
| Hereditary Risks | Family history indicating increased likelihood of lung cancer. |
| Screening Necessity | Importance of discussion with healthcare providers for preventive measures. |
Types of Lung Cancer Found in Non-Smokers
Knowing about lung cancers in non-smokers is key, as these aren’t always linked to smoking. Mainly, we see adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas in non-smokers. These types show different traits and start from different cells.
Adenocarcinomas and Their Characteristics
Adenocarcinomas take the lead among non-smokers’ lung cancers, making up 50-60% of cases. They start in the lung’s glandular cells. Compared to other lung cancers, they grow slower. Often, they’re caught early which helps in treating them effectively.
Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Others
Non-smokers get squamous cell carcinomas too, but less often, about 10-20% of cases. This cancer begins in the airways’ flat cells. Besides these, non-smokers can also get rarer cancers like carcinoid tumors. Each type needs a specific treatment plan, showing the varied nature of lung cancer.
| Type of Lung Cancer | Percentage in Non-Smokers | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Adenocarcinomas | 50-60% | Most common in non-smokers; glandular origin; slower growth. |
| Squamous Cell Carcinomas | 10-20% | Forms in flat airway lining cells; less common among non-smokers. |
| Carcinoid Tumors | Rare | Slow-growing; can be typical or atypical. |
Symptoms of Lung Cancer in Non-Smokers
Lung cancer has specific symptoms in non-smokers. Knowing these symptoms is key. This knowledge can help catch the disease early. Early-stage lung cancer shows several signs that we must not ignore.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Non-smokers should look out for certain signs. These signs may suggest lung cancer:
- Persistent cough
- Coughing up blood
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Hoarseness
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Wheezing
- Infections
As the cancer grows, symptoms can worsen. Patients may face bone pain or swelling of lymph nodes. These signs make seeking medical advice crucial.
Paraneoplastic syndromes may also appear. They can bring about issues in the endocrine and nervous systems. This could lead to conditions like Cushing syndrome. Spotting these signs early is essential for the right treatment.
Preventive Measures and Tips
Taking action early is key to lowering lung cancer risks. Simple steps can make a big difference in keeping your lungs healthy.
Testing for Radon in Homes
Radon is a top cause of lung cancer, especially in certain areas. It’s important for homeowners to check their homes for radon. If you find it, you can fix the problem to make your home safer.
Avoiding Secondhand Smoke
Avoiding smoke from others is crucial for lung health. Laws now help create spaces without smoke. It’s a good idea to stay away from places where people smoke. Doing so helps protect your lungs.
Conclusion
Lung cancer is now recognized in areas beyond smoking. It is vital to look at lung cancer with fresh eyes. We see more cases in people who have never smoked, driven by other factors. These include things like where you live and your genes.
This illness is now the fifth leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. It affects a lot of people who have never smoked. Understanding this can change how we approach lung health.
It’s very important to be aware, especially because more women and young people are getting lung cancer. In the U.S., 12% of lung cancer patients have never smoked. This shows everyone needs to be mindful of their health, smoking or not.
Learning about symptoms and taking steps to stay healthy can make a big difference. It helps handle the disease sooner if it happens.
As we learn more about lung cancer, staying updated and aware is key. Knowing more can lead to early finding and better treatment. This is especially true for lung cancer in non-smokers. It leads to better chances in fighting this disease.