Lung cancer is the top cause of cancer deaths in the United States. Surprisingly, it doesn’t just impact the lungs. Around 40% of those battling lung cancer might face pleural effusion. This means fluid builds up around their lungs. This issue makes breathing harder and points to a severe lung cancer complication. Through this guide, we aim to breakdown how lung cancer and lung fluid are connected. You’ll get to know about the symptoms, how doctors figure it out, and ways to treat it.
Lung cancer can show up in tricky ways, such as pleural effusion. For people at risk and their caregivers, knowing this is crucial. Early lung cancer signs are also vital to catch. Many mistake persistent coughs and breathing troubles for something less serious, like allergies. Over 50 million Americans deal with allergies yearly. These can seem similar to lung cancer signs. Telling them apart is essential for getting help early. Spotting these early signs can really make a difference in treatment, especially for those at greater risk.
In this guide, you’ll learn deeply about how lung cancer might cause pleural effusion. We’ll discuss what symptoms to look for and how to treat them. Knowing this information helps in dealing with lung cancer and its side effects more confidently.
Key Takeaways
- Approximately 40% of lung cancer patients may experience pleural effusion.
- Fluid in the lungs significantly complicates breathing and overall health.
- Recognizing early symptoms of lung cancer can enhance treatment efficacy.
- Managing lung cancer and related complications requires a multifaceted approach.
- Understanding the relationship between allergies and lung cancer symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis.
- Effective communication with healthcare providers can facilitate better management of lung cancer and its complications.
- Healthy lifestyle choices can help mitigate symptoms associated with lung cancer.
Understanding Lung Cancer and Its Symptoms
Lung cancer is a serious condition. It often stays hidden until it’s in its late stages. Knowing the symptoms is key for early finding and treatment.
Seeing these signs early on means doctors can step in sooner. This is key for better outcomes.
Lung Cancer Symptoms
Patients might notice several lung cancer symptoms that slowly appear. Early signs to watch for include:
- A persistent or severe cough that doesn’t go away.
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored spit.
- Chest pain that gets worse when you breathe deeply or cough.
- Hoarseness and changes in your voice.
- Unexplained weight loss and not feeling hungry.
- Constant shortness of breath and feeling tired.
- Getting sick often with things like bronchitis or pneumonia.
As cancer grows, symptoms can worsen and spread to other body parts. Quick action for these lung cancer symptoms boosts treatment success.
Common Causes and Risk Factors
Knowing the common causes of lung cancer and the risk factors helps in prevention. Some main causes include:
- Smoking tobacco is the top reason for lung cancer.
- Secondhand smoke exposure is also very harmful, especially to non-smokers.
- Past radiation therapy in the chest area for other health issues.
- Environmental dangers like radon gas.
- Working with asbestos.
- Having a family history of lung cancer increases your risk.
This knowledge can help people avoid risks and get regular check-ups if needed.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ihCnDjyJv5c
What is Pleural Effusion?
Pleural effusion is when there’s too much fluid between the lungs and chest wall. It makes breathing hard, affecting lung expansion. People must know the difference between normal and harmful pleural fluid to treat it right.
Definition of Pleural Effusion
Pleural effusion means fluid fills up the pleural space too much. This can happen for several reasons, like heart failure or cancer. When there’s too much fluid, symptoms like breathing trouble and chest pain appear.
Normal Pleural Fluid vs. Malignant Pleural Effusion
Normal pleural fluid helps your lungs move smoothly as you breathe. It’s usually clear and not much of it. But, if cancer breaks into the pleural area, the fluid increases and gets harmful. This bad turn often points to cancer and makes treating lung issues harder.
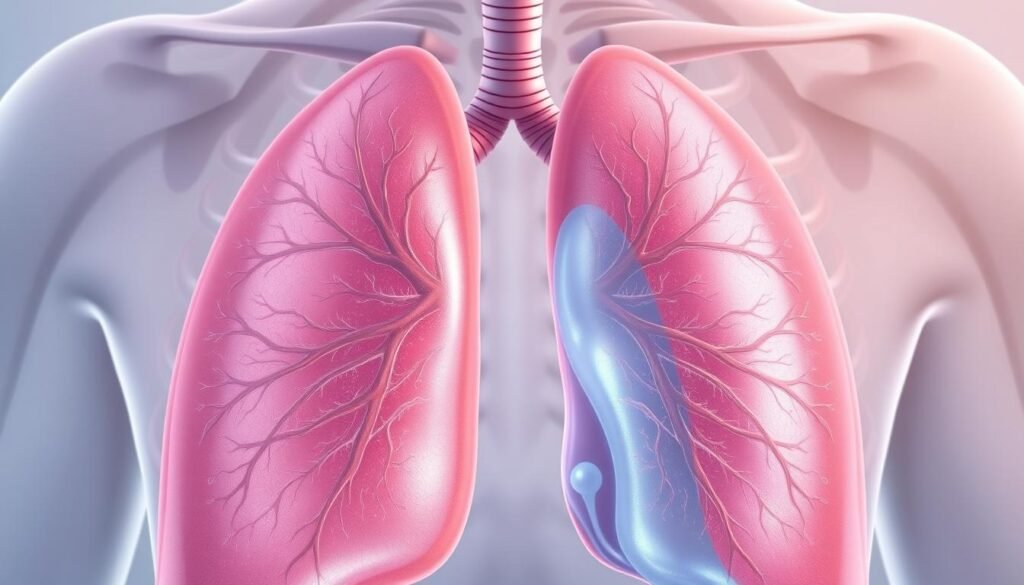
Can Lung Cancer Cause Fluid in the Lungs?
Knowing how lung cancer and fluid buildup are connected is crucial. Fluid accumulates because of the cancer, causing discomfort and health problems. This issue mainly involves the cancer’s impact on the pleura.
How Cancer Cells Lead to Fluid Buildup
Lung cancer can give rise to pleural effusion. This happens through the inflammation of the pleura. The growth of cancer cells messes with how fluid is managed in the body. This can either make too much fluid or block its drainage.
When fluid gathers, symptoms like breathing difficulties, chest pain, and coughing can appear. It is critical for people to keep an eye on their health. This situation confirms that lung cancer can indeed cause fluid in the lungs. A large number of lung cancer patients suffer from this condition, known as malignant pleural effusion.
Other Cancer Types Associated with Pleural Effusion
Breast cancer, mesothelioma, ovarian cancer, and non-Hodgkin lymphoma can also cause pleural effusion. These cancers disrupt the normal balance of pleural fluid. For example, breast cancer and mesothelioma are known to cause fluid buildup as well. Knowing these connections helps in recognizing symptoms and understanding cancer treatment better.
For more info on lung cancer effects and related issues, visit this resource.
Symptoms of Fluid Accumulation in the Lungs
It’s important to know the symptoms of fluid in the lungs. This helps spot serious issues like lung cancer early. The body shows warning signs when it’s time to see a doctor.
Shortness of Breath and Its Implications
Shortness of breath is a common sign of fluid in the lungs. It usually gets worse with activity or when you lie down. This means the lungs can’t hold as much air because of the fluid.
In serious cases, you might get acute pulmonary edema. This brings coughing, less ability to exercise, feeling anxious, and chest pain. Knowing these signs and getting help quickly is crucial.
Importance of Early Symptoms Detection
Finding lung cancer symptoms early is key to better health outcomes. Don’t ignore a constant cough or chest pain. Catching these signs early helps with getting the right diagnosis and treatment. Ignoring them makes breathing issues worse and increases risks from lung fluid.
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Shortness of Breath | Difficulty breathing, exacerbated by exertion or lying down |
| Cough | May be dry or produce pink, frothy sputum in acute cases |
| Decreased Exercise Tolerance | Inability to perform physical activities without experiencing breathlessness |
| Chest Pain | Discomfort in the chest area, which can accompany shortness of breath |
| Swelling in the Legs | Fluid retention in the lower extremities due to increased pressure in blood vessels |
Early recognition of these symptoms leads to better treatment of lung fluid issues.
Diagnosing Pleural Effusion
Doctors start diagnosing pleural effusion with a careful physical check. They look for signs of fluid in the pleural space. Then, they use tests to see if there is pleural effusion and how much.
Diagnostic Procedures Used
Doctors have several ways to diagnose pleural effusion:
- Chest X-rays: These are often the first test and can show extra fluid.
- Ultrasound: This test lets doctors see the fluid and plan what to do next.
- CT scans: These give a clearer picture of the fluid’s amount and type.
These tests are crucial for spotting pleural fluid. They show how much fluid there is. They also help find out if the cause might be serious, like malignant pleural effusion (MPE).
Understanding Imaging Techniques
Imaging is key for telling benign from serious causes. It leads the way for tests like thoracentesis, where fluid is examined closely. In MPE cases, imaging shows tumors and fluid tied to lung cancer problems. Choosing the right imaging method is vital for the patient’s treatment and care.
For more info on how doctors diagnose pleural effusion, there’s a review article. It explains the methods used, especially in lung cancer cases. You can read it here.
Treatment Options for Pleural Effusion
Lung cancer, especially the non-small cell type, often leads to pleural effusion. There are several treatments available aimed at easing symptoms and enhancing life quality. These methods are geared towards managing the condition effectively.
Draining the Fluid: Thoracentesis
Thoracentesis is a procedure that removes fluid from the pleural space with minimal invasion. It quickly eases symptoms such as difficulty in breathing. During this procedure, fluid samples are taken for testing to see if cancer cells are present. Decisions about further treatment are based on these results.
This method is typically the first step in treating pleural effusion.
Other Treatment Methods: Catheter and Pleurodesis
Besides thoracentesis, other treatments are available. Indwelling pleural catheters allow fluid to be drained continuously. They are ideal for patients dealing with repeated effusions. This method makes it easier for patients to manage their condition at home.
Pleurodesis is another technique used to stop fluid from building up again. It involves using a sclerosing agent like talc to cause an inflammation inside the pleural space. This seals the pleurae to prevent more effusions. Pleurodesis usually needs the patient to stay in the hospital overnight if a lot of fluid has to be removed first. How well it works can differ, and sometimes more than one procedure is needed.
| Treatment Method | Description | Hospitalization Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Thoracentesis | Minimally invasive fluid removal for immediate symptom relief | Outpatient |
| Indwelling Catheter | Encourages home drainage for recurrent pleural effusions | Outpatient |
| Pleurodesis | Sclerosing agent applied to prevent future fluid buildup | Average of 7 days |
For more info on malignant pleural effusion and its treatments, visit this source.
Living with Lung Cancer and Fluid in the Lungs
Living with lung cancer brings big challenges, especially with symptoms like shortness of breath and coughing. Learning how to cope can really help improve daily life. Supportive care is also key to making life better for lung cancer patients.
Coping with Symptoms like Dyspnea and Cough
Getting short of breath is common with lung cancer. Control breathing and finding the right way to sit or lie down can help. Also, doing breathing exercises regularly is good. If shortness of breath is very bad, using home oxygen can keep oxygen levels where they should be.
Supportive Care and Lifestyle Adjustments
Supportive care includes helping with both the body and mind. Lung cancer can cause feelings like worry and sadness. It helps to have support from experts and a group, including a lung cancer nurse. There is also money help for those who need time off work.
Personal care plans might have advice on eating right and physical therapy. Knowing why these changes matter can help patients handle their symptoms better.
Despite the tough parts of having lung cancer and fluid in the lungs, there are ways to make life better. Starting these steps helps build strength and aids in recovery.
| Coping Strategy | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Breathing Exercises | Techniques to improve lung function and reduce breathlessness | Enhanced lung expansion and reduced discomfort |
| Home Oxygen Therapy | Supplemental oxygen for severe breathlessness | Improved oxygen levels and quality of life |
| Emotional Support | Professional guidance and peer support | Decreased feelings of isolation and anxiety |
| Nutritional Guidance | Personalized eating plans to combat weight loss | Improved strength and overall health |
Potential Complications of Lung Cancer Treatments
It’s key to understand the lung cancer treatment complications for a patient’s health. After treatment, many encounter breathing problems due to the strong therapies used. These include chemotherapy and radiation, which can cause coughing, inflammation, and changes in how the lungs work. So, it’s vital to manage these side effects and help improve breathing health.
Post-treatment Effects on Breathing
After lung cancer treatment, many people find it hard to breathe. This is often because treatment causes lung inflammation. Help like respiratory therapy or medicines is critical for better lung function and comfort. Recognizing these issues leads to earlier intervention, providing needed support for patients.
Management of Malignant Pleural Effusion
About 15% of lung cancer patients develop malignant pleural effusion. In this condition, cancer moves to the pleural space, causing fluid buildup. A team effort by oncologists, pulmonologists, and care specialists is crucial in handling this. Treatments like thoracentesis not only remove this fluid but also help find its cause. Hence, adding methods to handle malignant pleural effusion is essential for patient care.