Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths all over the world. It’s responsible for almost 25% of all cancer deaths. Every year, lung cancer kills more people than colon, breast, and prostate cancers combined. Yet, many myths and misunderstandings about lung cancer still exist. These myths cause confusion about its causes, risk factors, and how to treat it. Around 20% of lung cancer deaths are in people who never smoked. Many people are unaware of the risks they face.
We want to clear up the myths and misconceptions about lung cancer in this article. By sharing the truth, we can fight the stigma and wrong information surrounding this disease. This can lead to better awareness and education. Let’s go through important facts about lung cancer, from its causes to why early detection and screening are vital.
Key Takeaways
- Lung cancer leads to more deaths than the three most common cancers combined.
- About 20% of lung cancer fatalities occur in non-smokers.
- Myths regarding lung cancer can hinder prevention and diagnosis.
- Awareness and education are crucial for effective lung cancer management.
- Understanding accurate lung cancer facts helps in combating harmful stigmas.
- Early detection through screening can significantly lower lung cancer mortality rates.
Introduction to Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is the top cause of cancer deaths globally. It mainly starts in the lung tissues, specifically in the cells within the airways. As we learn more, our understanding lung cancer grows, especially about what leads to it.
Lung cancer deeply affects patients and their families emotionally. Many get confused by myths about its causes and risks. Education is critical in fighting these misconceptions. With the right information, patients can better handle their condition and choices in treatment. They’re urged to find dependable resources for lung cancer introduction to reduce unnecessary fear and anxiety.
It’s key to know not all lung cancer comes from smoking. Though smoking is a major risk, about 10% of patients, including 20% of women, never smoked. This fact shows we need to consider many factors when looking at risks. Knowing the true risks helps everyone make better choices and promotes prevention.
Understanding Lung Cancer Facts
Lung cancer is a key health issue with many facets. About 10% to 20% of lung cancers are in non-smokers. This includes those who have never smoked. This shows the need for detailed lung cancer information beyond smoking as the only risk. Being around secondhand smoke raises the risk of lung cancer by 20% to 30%. This shows its effect on health.
Statistically, 1 in 15 men and 1 in 17 women may face lung cancer. The average age for diagnosis is 73. However, it’s key to know that younger people and non-smokers can get it too. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) makes up 80% to 85% of cases. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is the most aggressive form.
Early lung cancer can often be cured, with 60% to 90% cured by surgery alone. For those who can’t have surgery, 20% of them with advanced stage 3 lung cancer may be cured. They can be cured using chemo or radiation. Factors like secondhand smoke, radon gas, and pollution can cause lung cancer in non-smokers.
Lately, more young adults and non-smokers are being diagnosed with lung cancer. Staying away from tobacco smoke and reducing exposure to toxins can lower the risk a lot. This highlights how vital it is to know the facts about lung cancer. It also shows how treatment and survival rates have improved. These improvements come from early detection and therapy advancements.
Lung Cancer Causes: Beyond Smoking
Lung cancer’s causes go beyond the well-known link to smoking. It’s vital to know all the causes to prevent and be aware. While smoking is top of the list, many environmental factors also up the risk.
Radon and Other Environmental Factors
Radon is a colorless gas that comes from soil and rocks, and it’s a big cause of lung cancer in non-smokers. This gas can get into buildings and is dangerous in places without good air flow. It’s important to check homes for radon to lower the risk. Pollution and chemicals in the environment also make lung cancer more likely.
Role of Secondhand Smoke
Being around smoke when you don’t smoke increases lung cancer risk by 20% to 30%. This is a big worry in places where people smoke, like some homes and work spots. Making these areas smoke-free is key to keeping non-smokers safe from dangerous smoke.
Occupational Hazards and Carcinogens
Jobs that expose people to harmful substances add another risk for lung cancer. Things like asbestos, arsenic, and diesel fumes in some workplaces can make people more likely to get sick. Safe work practices and rules are important to cut down on these dangers.
| Environmental Factors | Effects on Lung Cancer Risk |
|---|---|
| Radon | Major contributor in non-smokers, requires home testing |
| Secondhand Smoke | Increases risk by 20% to 30% for non-smokers |
| Occupational Exposure | Exposure to carcinogens like asbestos increases risk |
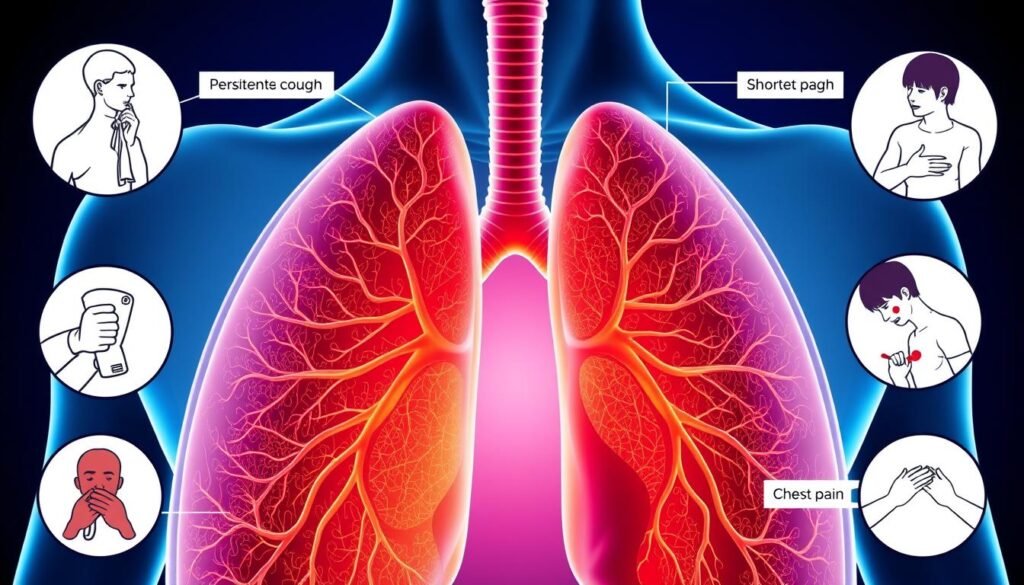
Lung Cancer Symptoms You Should Know
Knowing the signs of lung cancer is key to getting help early. People might notice various symptoms that can be easy to ignore. Common symptoms like a lasting cough, pain in the chest, and trouble breathing are important to watch for. Other signs, such as swelling in the fingers or losing weight without trying, can also indicate lung cancer. Spotting these early can make a big difference, as lung cancer doesn’t always show signs at first.
Common Symptoms vs. Rare Symptoms
The common symptoms of lung cancer often include:
- A cough that gets worse and doesn’t go away
- Chest pain that increases with deep breaths or coughing
- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Getting lung infections, like pneumonia, often
- Losing weight without trying
Other, less common signs that some people might experience are:
- Feeling very tired even after resting
- Not wanting to eat
- Seeing blood when coughing
- Swelling in the face or neck
Importance of Early Detection
Finding lung cancer early can greatly improve the chances of successful treatment. Yet, the vague nature of early signs means they’re often missed. Screenings are especially important for those between 50 and 80 years old who have smoked a lot. The latest guidelines now mean five million more people can get screened. This is a push towards catching lung cancer early, before it gets worse.
Recognizing Lung Cancer Risk Factors
Knowing what increases lung cancer risk is key to prevention. Smoking and tobacco are well-known causes, but other factors matter too. Understanding these can shape better prevention efforts.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Smoking is the top cause of lung cancer, linked to 80% of deaths. But there’s a twist – not all victims are smokers. This highlights the need to know other risk factors too. Quitting smoking cuts lung cancer risk significantly, boosting overall health.
Age and Gender Considerations
Lung cancer can hit anyone, at any age or gender. Most people are diagnosed around 70, but younger adults aren’t immune. Men and women face different odds of getting lung cancer, influenced by genetics and hormones too. Alarmingly, lung cancer is the deadliest cancer, claiming lives regardless of smoking status.
Lung Cancer Myths and Misconceptions
It’s crucial to bust myths about lung cancer to boost awareness. Many wrong beliefs block the truth and spark stigma. We need to correct these ideas to help people understand and care more.
Myth: Only Smokers Get Lung Cancer
Many think only smokers get lung cancer. But, 10% to 20% of cases are in non-smokers, says the CDC. Many non-smoking-related factors can cause it. We should consider all risk factors.
Myth: Lung Cancer Mainly Affects Men
Once, more men got lung cancer than women. Now, more women, especially non-smokers, are getting it too. This change means we need to dump old gender ideas for better awareness and care.
Myth: All Lung Cancers Are the Same
Thinking all lung cancers are the same is wrong. There are types like non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Each type is different and needs its own treatment. Knowing these differences helps in giving the right care.
Myth: A Cough Is a Guaranteed Symptom
Many link lung cancer to a constant cough. Yet, not everyone with lung cancer coughs. In fact, half don’t have a cough. It’s key to know all symptoms and risks for early finding and treatment.
We have to fight lung cancer myths and wrong ideas. Sharing correct information from truthful sources helps a lot. This way, we can better support those with the disease and create a caring community.
Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines
Lung cancer is the top cause of cancer deaths in the United States. This makes it vital to catch it early through screening. The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force sets rules for lung cancer tests. These rules help find lung cancer sooner. They say people 50 to 80 who smoke or quit within the last 15 years should get yearly low-dose CT scans. They also need a history of 20 pack-years of smoking.
A pack-year is how much someone has smoked over time. For instance, a pack a day for 20 years equals 20 pack-years. Low-dose CT scans use much less radiation than regular CT scans. They also take about ten minutes, making them fast and easy.
Many health plans cover lung cancer screenings. This includes Medicare, Medicaid, and most private insurance, at no extra cost if you’re eligible. If you don’t have insurance, some places offer low-cost tests. Yet, lots of people who could benefit from screening don’t know about it. Others believe myths about screening and don’t get tested.
The American Cancer Society wants more people to get screened for lung cancer. They now say anyone who has ever smoked should consider annual screening. This can help find lung cancer early. Finding it early may improve the chances of beating the disease for those at high risk.
| Eligibility Criteria | Annual Screening Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Age 50-80 | Yes |
| Current Smoker or Quit within Last 15 Years | Yes |
| 20 Pack-Year Smoking History | Yes |
| Insurance Coverage | Medicare, Medicaid, Most Private Plans |
| Self-Pay Options | Available |
Following these lung cancer testing guidelines helps people protect their health. Taking action early can lead to a better chance at successful treatment if cancer is found.
Lung Cancer Treatment Options Explained
Lung cancer treatment uses different methods to care for patients’ unique needs. Treatment choices are made by a team. This team looks at the cancer’s stage, location, and the patient’s health. Understanding all options for lung cancer can help people. It makes them aware of the therapies they can choose from.
Role of Surgery and Radiation
Surgery is key in treating lung cancer. It removes the cancer and might lead to recovery. Radiation often helps surgery, especially in late stages. It uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Doctors are always working to make these treatments better and safer.
Effectiveness of Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy
Chemotherapy and radiation are main ways to treat lung cancer. Chemotherapy controls tumor growth. Newer treatments like immunotherapy use the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Together, they show promising results, especially for advanced cancer. Testing the cancer’s genes can make treatments even more effective. Patients should talk with their doctors to choose the best option. To learn more about lung cancer treatments, visit this informative source.
Lung Cancer Prevention Strategies
Lung cancer prevention is key in fighting this disease. It’s vital to adopt strategies that boost health and cut lung cancer risks. Knowing how to stop smoking and avoid environmental dangers is essential.
Importance of Quitting Smoking
Stopping smoking is a top way to lower lung cancer risk. Benefits include better lung function and more oxygen in your blood. If you don’t smoke, your body starts to heal. This drops your lung cancer risk as time goes on.
For help, smokers can look into the Genesis Tobacco Treatment Program. It offers customized help to quit smoking, improving your chance to quit for good.
Reducing Exposure to Risk Factors
It’s important to limit exposure to environmental and workplace risks. Knowing about dangers like radon and pollutants helps. Making smart choices reduces your risks.
- Test your home for radon regularly.
- Use air purifiers to clean indoor air.
- Wear protective gear at work if needed.
Taking these steps, along with living healthily and knowing about lung cancer, puts your health in your hands. It greatly lowers your lung cancer risk.
| Strategy | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Quitting Smoking | Improves lung function, decreases cancer risk over time. |
| Reducing Radon Exposure | Minimizes one of the leading causes of lung cancer. |
| Healthy Diet | Provides nutrients that support overall lung health. |
| Regular Exercise | Enhances lung capacity and general health. |
Lung Cancer Statistics You Should Know
Lung cancer insights reveal a significant global impact. In 2022, about 2,480,675 people were diagnosed worldwide. The highest rate was in China, with 40.8 cases per 100,000 people. Meanwhile, the United States saw 226,033 new cases, showing the disease’s strong presence.
Incidence Rates by Demographics
Incidence rates vary by demographics. Men have higher rates than women. Hungary and New Caledonia have the highest lung cancer rates. Globally, lung cancer is the third most common cancer for both sexes. It led to 1,817,469 deaths in 2022, making it highly fatal.
Survival Rates Over the Years
Survival rates have been improving thanks to new treatments and early detection. Most cases were historically spotted at stage 4, resulting in low survival rates. However, better medical care is now leading to more positive outcomes. Ongoing research aims to further increase survival and offer hope to patients.
Lung Cancer Awareness and Education
Lung cancer awareness is key in battling this common illness. Groups like the American Society of Clinical Oncology, with over 30,000 members, aim to better cancer care. They focus on community efforts to teach about lung cancer and offer needed resources. This helps clear up myths about the disease.
Campaigns push for more people to learn about lung cancer. The American Thoracic Society has over 15,000 members working hard. They want to increase knowledge of lung diseases, including lung cancer. Their goal is to spread true facts to families, communities, and schools.
Stats show why this work is so important. This year, around 238,340 people will get lung cancer, and about 127,070 will die from it. Lung cancer causes 1 out of every 5 cancer deaths. So, teaching about it is a top priority for groups like the Oncology Nursing Society. This society has more than 35,000 nurses.
Community lung cancer efforts not only teach but also help create support networks. These networks help patients and their families. Getting the community involved can lead to spotting the disease early and better chances of beating it. Together, we can fight this deadly disease.
Conclusion
It’s vital to understand lung cancer to fight the myths that hinder prevention and early detection. This article has underlined the need for awareness of lung cancer. It’s a mistake to think only smokers or men get lung cancer. About 15% of lung cancer cases happen to people who’ve never smoked. This shows us that other risks like radon and secondhand smoke are important too.
Statistics show that early detection, like with low-dose CT scans, boosts survival rates. This is especially true for women caught early. Everyone should keep an eye on their health and learn more about lung cancer. Young people and non-smokers can get lung cancer too. This highlights the importance of early screening and making healthy lifestyle choices.
We need to educate communities about lung cancer to fight stigma and raise awareness. For more information and to bust more lung cancer myths, check out Beaumont Health. By spreading the word and taking informed steps, we can achieve better health outcomes for everyone.